Did you know that over 75% of soft-tissue treatments utilize hyaluronic acid (HA) dermal fillers? The American Society of Plastic Surgeons reports this increase in minimally invasive procedures, reflecting a growing interest in HA injectables among individuals seeking aesthetic enhancements.
Hyaluronic acid dermal fillers rejuvenate the skin by restoring its plumpness and smoothness. Notably, Neuramis and Juvederm injectables excel in this field. These brands have developed fillers specifically designed to volumize, contour, and lift targeted facial areas, including the cheeks, lips, and jawline.
In this article, we will explore the differences between Neuramis filler vs Juvederm injections, including their formulations, injection techniques, treatment areas, and longevity, to help you make an informed choice for your aesthetic needs.
Key Takeaways
- Neuramis and Juvederm’s unique formulations make them well-known dermal filler brands that can effectively target individuals’ facial skin problems.
- Both injectables use hyaluronic acid as their primary active ingredient but differ in their cross-linking technologies.
- Administration of these dermal fillers significantly affects patient experience and results.
- Each dermal filler in the Neuramis and Juvederm collection offers specific targets for skin concerns and treatment areas.
- Neuramis dermal fillers can last between nine to twelve months, while Juvederm fillers offer a longer duration of 12 months or longer.
About: Medica Depot is your trusted all-in-one supplier, offering a range of high-quality medical injectables and supplies. Buy Neuramis online at Medica Depot today! Whether for health professionals, plastic surgeons, dermatologists, licensed estheticians, or other specialists, we can offer genuine, brand-name products you may need. With Medica Depot, we prioritize serving you better to improve the patient’s quality of life.
Introduction to Neuramis and Juvederm Fillers
South Korean aesthetic company Medytox developed Neuramis fillers to address various skin concerns experienced by individuals. They offer a collection of Neuramis dermal fillers, including Neuramis, Neuramis Light, Neuramis Deep, and Neuramis Volume.
Similarly, Allergan produced Juvederm fillers to treat facial skin concerns, specifically those of aging individuals who wish to enhance their appearance. The Juvederm dermal fillers collection consists of six injectables: Voluma XC, Volux XC, Vollure XC, Volbella XC, Ultra XC, and Ultra Plus XC.
Importance of Choosing the Right Filler for Aesthetic Goals
Selecting the appropriate filler is crucial for achieving optimal aesthetic outcomes. While both Neuramis and Juvederm can deliver impressive rejuvenation, the choice between them depends on individual needs—such as the desired treatment area, the extent of volume enhancement required, and personal skin characteristics.
The right choice can not only achieve the best results but also minimize potential risks and ensure a satisfying and natural-looking outcome.
Formulation Differences
When comparing Neuramis vs Restylane or Neuramis filler vs Juvederm, individuals should understand the differences in their formulations. Aesthetic providers must discuss this factor and determine which solution best aligns with the patient’s skin type, condition, treatment area, and individual goals.
Neuramis uses non-animal hyaluronic acid cross-linked with SHAPE technology, which involves a two-step cross-linking process. This method provides an extended duration of effects, enhancing the filler’s longevity. Additionally, Neuramis has high purity and biocompatibility, making it suitable for individuals with sensitive skin. Many Neuramis formulations also contain lidocaine to reduce discomfort during injections.
Juvederm also utilizes hyaluronic acid, which is a naturally occurring substance in the skin. The Vycross cross-linking technology employed by Juvederm ensures a smooth gel consistency that spreads evenly under the skin. This results in a natural feel and a softer texture, enhancing patient comfort during and after the procedure. Some Juvederm fillers also contain lidocaine to minimize pain.
Both injectables use hyaluronic acid as their primary active ingredient but differ in their cross-linking technologies. Neuramis’s technology ensures longer-lasting results, while Juvederm’s unique process assures a smooth gel consistency. These technologies may have different goals, but Neuramis and Juvederm can address facial aging signs efficiently.
Injection Techniques
The injection techniques for Neuramis and Juvederm fillers vary based on the specific concerns, skin type, and aesthetic goals of the patient. A qualified and licensed aesthetic provider will determine the most suitable approach for optimal outcomes.
For Neuramis, below are some of the common techniques used to administer this filler:
- Ultra Thin Wall (UTW) Needles: Neuramis fillers typically require Ultra Thin Wall needles for precision and reduced discomfort.
- Multiple Small Injections: Practitioners often use multiple small injections to ensure an even product distribution and natural-looking results.
- Linear Threading and Serial Puncture Techniques: These are commonly used methods to create consistent results. Linear threading effectively treats larger areas, while serial puncture allows for better control in smaller, targeted regions.
For Juvederm, here are the techniques experts follow:
- Needle or Cannula: Depending on the treatment area, Juvederm fillers can be administered using either a needle or a blunt-tip cannula. The choice depends on the level of precision required and the risk of bruising.
- Techniques Used: Practitioners may employ techniques such as tunneling, fanning, crosshatching, or ferning. These methods help ensure smooth and even distribution, enhancing the natural feel and minimizing any visible inconsistencies.
Recommended Treatment Areas
Neuramis fillers, originating from South Korea, are often used to enhance facial volume and reduce visible signs of aging in various areas. Typical treatment areas include:
- Delicate Facial Regions: Such as the under-eye area for reducing dark circles.
- Chin and Cheeks: To improve definition and restore lost volume.
- Lips: Enhancing shape and fullness.
- Forehead: Addressing fine lines and maintaining smoothness.
Meanwhile, the Juvederm collection by Allergan is FDA-approved and well-known for treating a variety of concerns, with an emphasis on adding volume and creating a smooth texture:
- Cheeks and Jawline: To lift and contour facial features, providing a more sculpted appearance.
- Chin: Enhancing projection and balancing facial proportions.
- Lips: Creating a fuller, natural-looking pout.
Differences and Implications for Patient Satisfaction
The versatility of both injectable brands makes them suitable for different treatment areas, but the choice between Neuramis and Juvederm often depends on the unique formulations and intended uses:
- Neuramis is formulated with highly purified hyaluronic acid, making it suitable for individuals with sensitive skin who are looking for safe and effective volume enhancement. Its application in delicate areas such as the under-eye or forehead is ideal for subtle improvements, contributing to higher satisfaction for patients with sensitive skin.
- Juvederm’s smooth consistency ensures more uniform results, making it an excellent choice for areas requiring a natural but noticeable lift, such as the cheeks and jawline. This property is particularly valuable for patients seeking a refined but transformative effect.
Effectiveness, Longevity, and Patient Satisfaction
Individuals can expect Neuramis fillers to help them achieve their aesthetic goals. The formulation ensures smooth, natural-looking results that target visible facial aging signs and address volumization and contouring in various facial areas. The proper administration by aesthetic professionals can lead to even distribution and prevent complications.
Neuramis dermal fillers can last between nine to twelve months. In contrast, Juvederm fillers offer a longer duration of 12 months or longer. The longevity of both fillers depends on the specific formulation, dosage, administration, and individual characteristics, such as skin type, metabolism, and severity of skin condition.
Clinical Studies and Patient Experiences
A controlled trial proved that Neuramis Deep is equally effective as Restylane in improving nasolabial folds. The study found no significant difference in efficacy between the two fillers. These results suggest Neuramis Deep is a safe and effective option for enhancing nasolabial folds.
A randomized controlled trial demonstrated that Juvederm injectable gel offers reliable, long-term correction. Juvederm Ultra typically lasts over nine months, while Juvederm Ultra Plus can maintain results for a year or more.
While specific patient satisfaction rates and before-and-after photos for Neuramis are limited online, Juvederm has numerous visual evidence of patients who have received the efficacy of their treatments. Additionally, these patients achieve natural-looking results for their lips and minimal downtime associated with Neuramis and Juvederm, respectively.
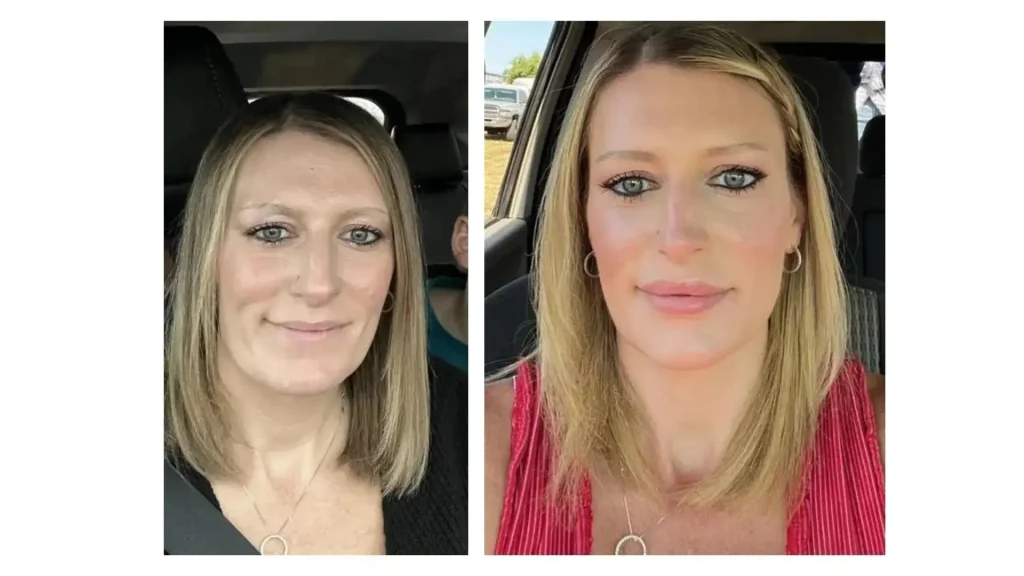


While these patients have received safe and effective treatments of Neuramis and Juvederm, it’s worth noting that individuals should seek the expertise and guidance of medical professionals before proceeding. They can ensure patient suitability, safety, and the efficacy of the products.
Conclusion
The comparison between Neuramis vs Juvederm helps individuals choose the most suitable dermal filler for their aesthetic goals. Though they differ in formulation, injection techniques, and treatment areas, both offer safe and effective results.
Consulting a qualified aesthetic professional is essential for making informed decisions based on individual skin types and goals, ensuring optimal outcomes and safety. Tailored treatment plans, guided by experienced providers, are key to achieving the best possible enhancements.
FAQs
1. What are the main differences between Neuramis and Juvederm fillers?
Neuramis and Juvederm fillers have different formulations. Neuramis utilizes non-animal hyaluronic acid cross-linked using SHAPE technology, while Juvederm utilizes Vycross cross-linking technology. They also differ in their injection techniques and recommended treatment areas.
2. Which filler brand is more suitable for sensitive skin types?
Neuramis fillers are known for their high purity and biocompatibility, making them suitable for individuals with sensitive skin or other skin types. Additionally, some Neuramis injections contain lidocaine to minimize discomfort during the injection procedure.
3. How can patients determine which filler is best for them?
Patients should consult their trusted aesthetic professionals for recommendations and knowledge to determine which filler best suits their aesthetic goals and skin type. Choosing the suitable filler with the guidance of a professional can help achieve the best results and ensure overall satisfaction with the procedure.
References
- American Society of Plastic Surgeons. (2020). PLASTIC SURGERY STATISTICS REPORT 2020. https://www.plasticsurgery.org/documents/News/Statistics/2020/plastic-surgery-statistics-full-report-2020.pdf
- Pak, C., Park, J., Hong, J., Jeong, J., Bang, S., & Heo, C. Y. (2015). A Phase III, Randomized, Multi-Center, Double-Masked, Matched-Pairs, Active-Controlled Trial to Compare the Efficacy and Safety between Neuramis Deep and Restylane in the Correction of Nasolabial Folds. Archives of plastic surgery, 42(6), 721–728. https://doi.org/10.5999/aps.2015.42.6.721