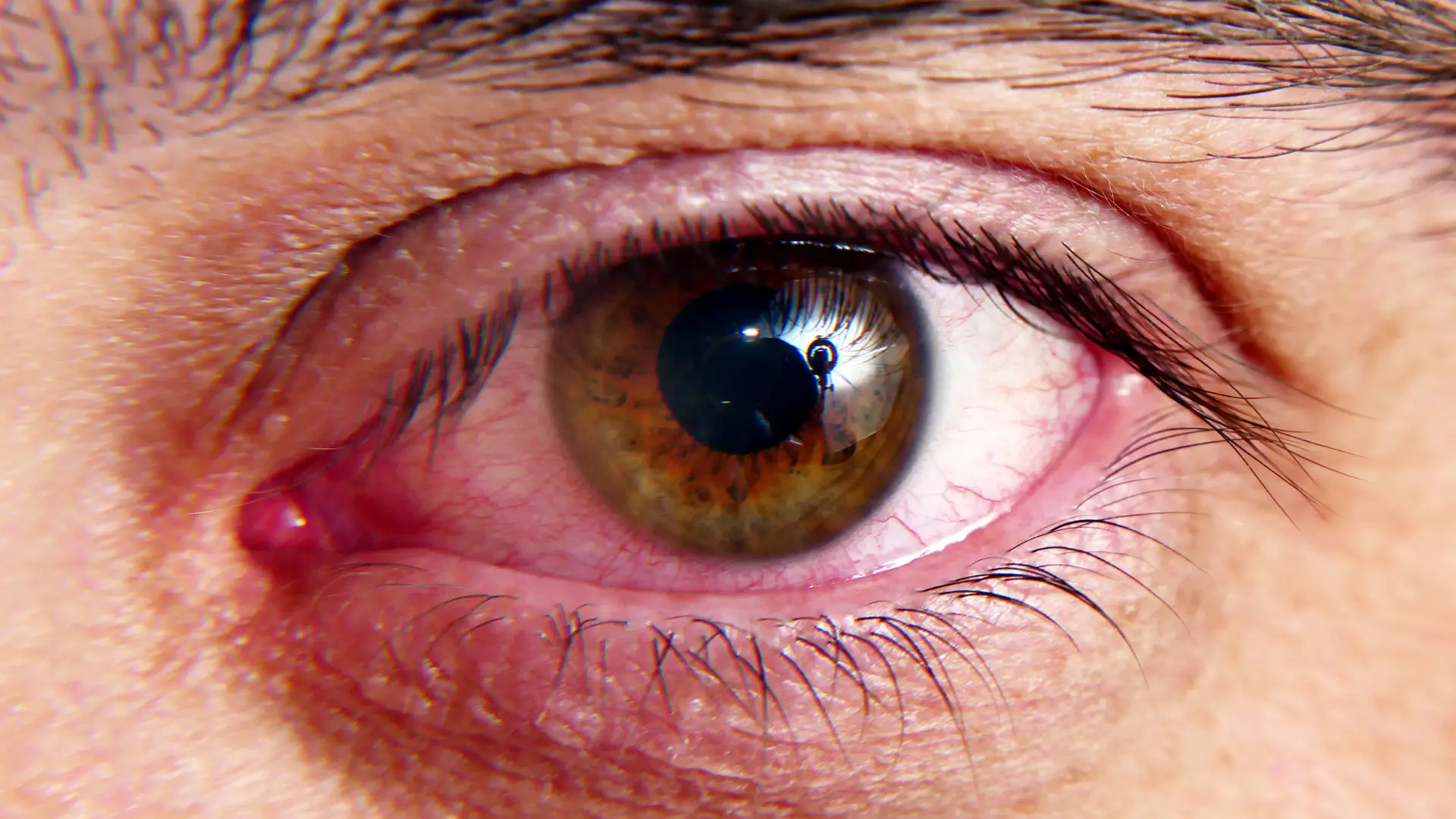
Lumigan (bimatoprost ophthalmic solution) is a widely used treatment for glaucoma and ocular hypertension. It effectively reduces intraocular pressure (IOP) to help prevent vision loss. Clinical trials have confirmed its efficacy and safety, making it a reliable choice for many patients.
However, like any medication, Lumigan comes with potential side effects, some of which may be unexpected or even permanent. One of the most well-known effects is a gradual change in eye color, as prolonged use can cause increased brown pigmentation in the iris. Patients may also experience common side effects such as eye redness, irritation, eyelash growth, and rarer systemic reactions.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at Lumigan side effects, including permanent changes, common and systemic symptoms, potential risk factors, and why patient consultations are crucial for safe use.
Key Takeaways
- Lumigan medicine effectively lowers intraocular pressure in patients with glaucoma, but its potential side effects should be carefully considered.
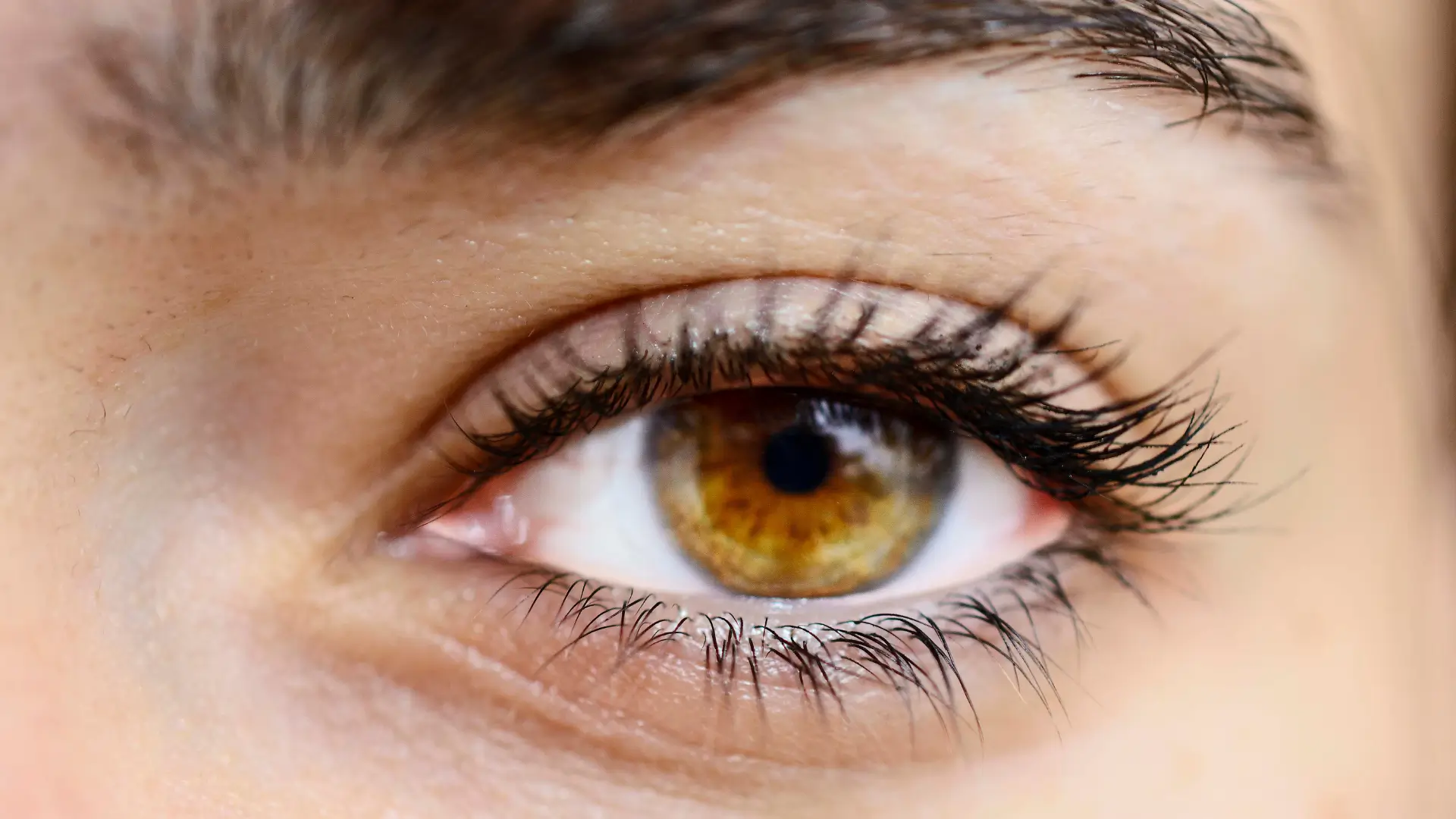
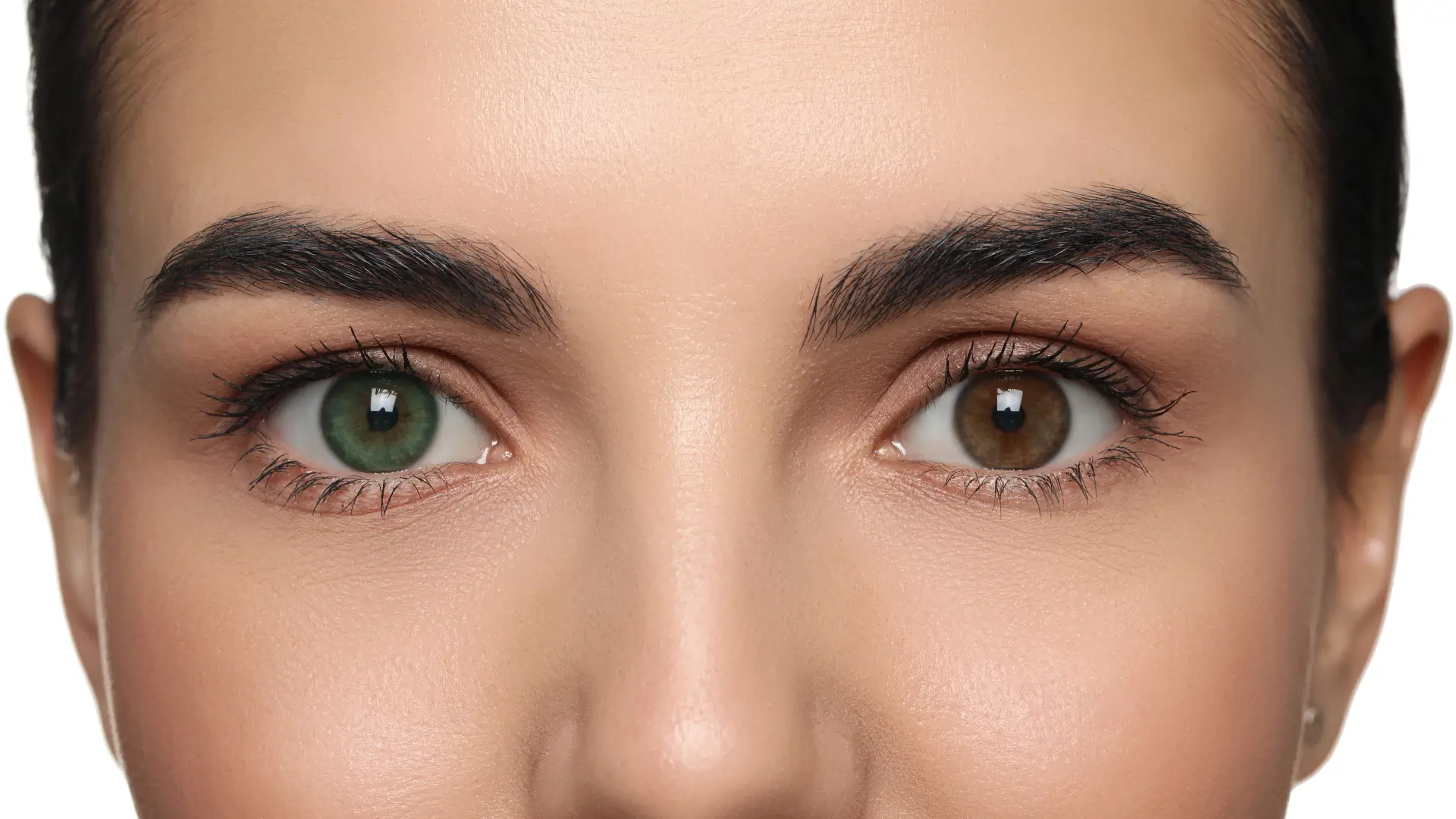
- A significant side effect is permanent eye color changes, caused by increased melanin production in the iris.
- Common ocular side effects include redness, irritation, and skin discoloration around the eyes, which may require medical attention.
- Patients should be aware of their risk factors and consult their healthcare provider regularly to monitor and manage any adverse effects.
About: Medica Depot is your trusted all-in-one supplier, offering a range of high-quality medical injectables and supplies. Buy Lumigan online at Medica Depot today! Whether for health professionals, plastic surgeons, dermatologists, licensed estheticians, or other specialists, we can offer genuine, brand-name products you may need. With Medica Depot, we prioritize serving you better to improve the patient’s quality of life.
Mechanism Behind Iris Pigmentation Changes
The OCA2 and HERC2 genes influence melanin levels and primarily determine iris color. The iris has two layers: stroma and epithelium. Variations in these layers’ melanin levels and environmental factors like sunlight exposure can affect eye color changes. When these genes are less active, less melanin is produced, resulting in lighter eye colors like blue or green.
Bimatoprost, found in medications like Lumigan, boosts melanin production in the iris. This prostaglandin analog primarily treats glaucoma and indirectly promotes eyelash growth. However, practitioners and patients must know that the reported Lumigan side effects include gradual iris darkening and iris color changes.
- Iris Darkening: It stimulates melanocytes, producing melanin and increasing pigmentation.
- Iris Color Change: This side effect is usually permanent, as bimatoprost increases the melanin levels, and the color change is typically irreversible.
Given the permanence of these changes, it is crucial to understand the potential side effects and discuss them with a trusted and licensed healthcare provider before starting treatment. A doctor can prescribe Lumigan to those with glaucoma open angle or ocular hypertension and intraocular hypertension.
Common Ocular Side Effects
Healthcare professionals play a crucial role in ensuring patients clearly understand Lumigan’s potential side effects. Open discussions about these effects allow patients to make informed decisions and monitor their eye health throughout treatment.
- Conjunctival Hyperemia: The dilation of blood vessels in the conjunctiva can cause visible redness, making the eyes appear irritated.
- Ocular Irritation & Discomfort: Some patients experience dryness, burning, itching, or a gritty sensation, which can impact daily comfort.
- Periorbital Skin Darkening: Prolonged use of Lumigan may darken the skin around the eyes, including the eyelid, often due to hyperpigmentation or post-inflammatory changes.
While these reactions are generally mild, patients should be aware of more serious concerns, such as allergic reaction to Lumigan, which may cause severe eye irritation, swelling, or difficulty breathing. Other rare but severe concerns include macular edema, which involves distorted or blurred vision. If any unusual symptoms occur, it’s essential to seek immediate medical attention.
Regular eye health monitoring and open communication with healthcare providers help patients manage side effects effectively and ensure safe, long-term use of Lumigan for the eye.
Systemic Side Effects

Medications like Lumigan can cause systemic side effects that affect areas beyond the application site or the eye. While these reactions are less common, they can still impact overall health and well-being. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s recommendations for managing symptoms and seek medical advice if side effects persist or worsen.
- Respiratory Issues: Some individuals may experience coughing, difficulty breathing, or nasal congestion, which can cause discomfort and breathing difficulties.
- Headaches: Ranging from mild to severe, headaches can affect daily activities and overall quality of life.
Risk Factors for Adverse Effects
A thorough consultation with a medical professional is essential to ensure patient safety and suitability for Lumigan treatments. A personalized treatment plan helps maximize effectiveness while minimizing potential risks. Practitioners must also evaluate key risk factors that may influence adverse effects in ocular treatments, such as:
- Patient Demographics: Factors such as age, gender, and ethnicity can impact the likelihood and severity of side effects. For example, older adults may be more prone to ocular changes that affect treatment response. Additionally, socioeconomic factors can influence treatment accessibility and outcomes.
- Pre-Existing Conditions: Patients with diabetes, hypertension, or autoimmune diseases may experience more pronounced side effects due to altered medication metabolism and increased complication risks.
Patient Counseling and Management Strategies
Educating patients about potential side effects is essential to ensuring they understand their treatment and can promptly recognize any adverse reactions. Healthcare providers should offer clear and concise guidance on expected Lumigan side effects, management strategies, and when to seek medical attention. This patient-centered approach promotes better treatment adherence and improved health outcomes.
Beyond education, regular monitoring and personalized treatment plans play a crucial role in managing potential risks. Follow-up consultations allow medical professionals to assess patients’ responses to treatment, address concerns, and adjust care plans as needed. Early detection and intervention can minimize side effects and ensure a smoother treatment experience.
Other tips that can help in achieving optimal outcomes include:
- Maintain open communication between patients and healthcare providers.
- Ensure timely intervention and support if side effects arise.
- Follow proper post-treatment care to maximize effectiveness and minimize risks.
Conclusion
While Lumigan is highly effective in managing glaucoma and ocular hypertension, patients should be aware of its potential side effects. Permanent eye color changes due to increased melanin production, along with other ocular and systemic reactions, may occur. Understanding these risks allows patients to make informed decisions about their treatment.
Open communication with healthcare providers is essential for early detection and management of side effects. Patients should feel encouraged to discuss any concerns or unusual symptoms, ensuring that their eye health and overall well-being remain a priority.
By staying informed, proactive, and engaged in their care, patients can maximize the benefits of Lumigan while minimizing potential risks, leading to a safer and more comfortable treatment experience.
FAQs
1. What is Lumigan, and how does it work?
Lumigan is a prescription eye drop solution or medicine containing bimatoprost used to treat glaucoma and ocular hypertension. It works by increasing fluid drainage from the eye, which helps lower intraocular pressure.
2. Can Lumigan change patients’ eye color?
Yes, one of the notable side effects of Lumigan is the potential for iris darkening and color changes. This effect is usually permanent due to increased melanin production in the iris.
3. What are some common side effects of Lumigan?
Similar to any medicine, side effects may occur. Common side effects include conjunctival hyperemia (redness of the eye), ocular irritation (dryness, burning, or itching), and skin darkening around the eyes, like eyelid. Patients should consult their healthcare provider if they experience any uncomfortable symptoms.
References
- Day, D. G., Walters, T. R., Schwartz, G. F., Mundorf, T. K., Liu, C., Schiffman, R. M., & Bejanian, M. (2013). Bimatoprost 0.03% preservative-free ophthalmic solution versus bimatoprost 0.03% ophthalmic solution (Lumigan) for glaucoma or ocular hypertension: a 12-week, randomised, double-masked trial. British Journal of Ophthalmology, 97(8), 989–993. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjophthalmol-2012-303040
- Pharma Academias. (2024, December 12). Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) Reporting and Management – Pharmaacademias. Pharmaacademias. https://www.pharmaacademias.com/adverse-drug-reaction-adr-reporting-and-management/