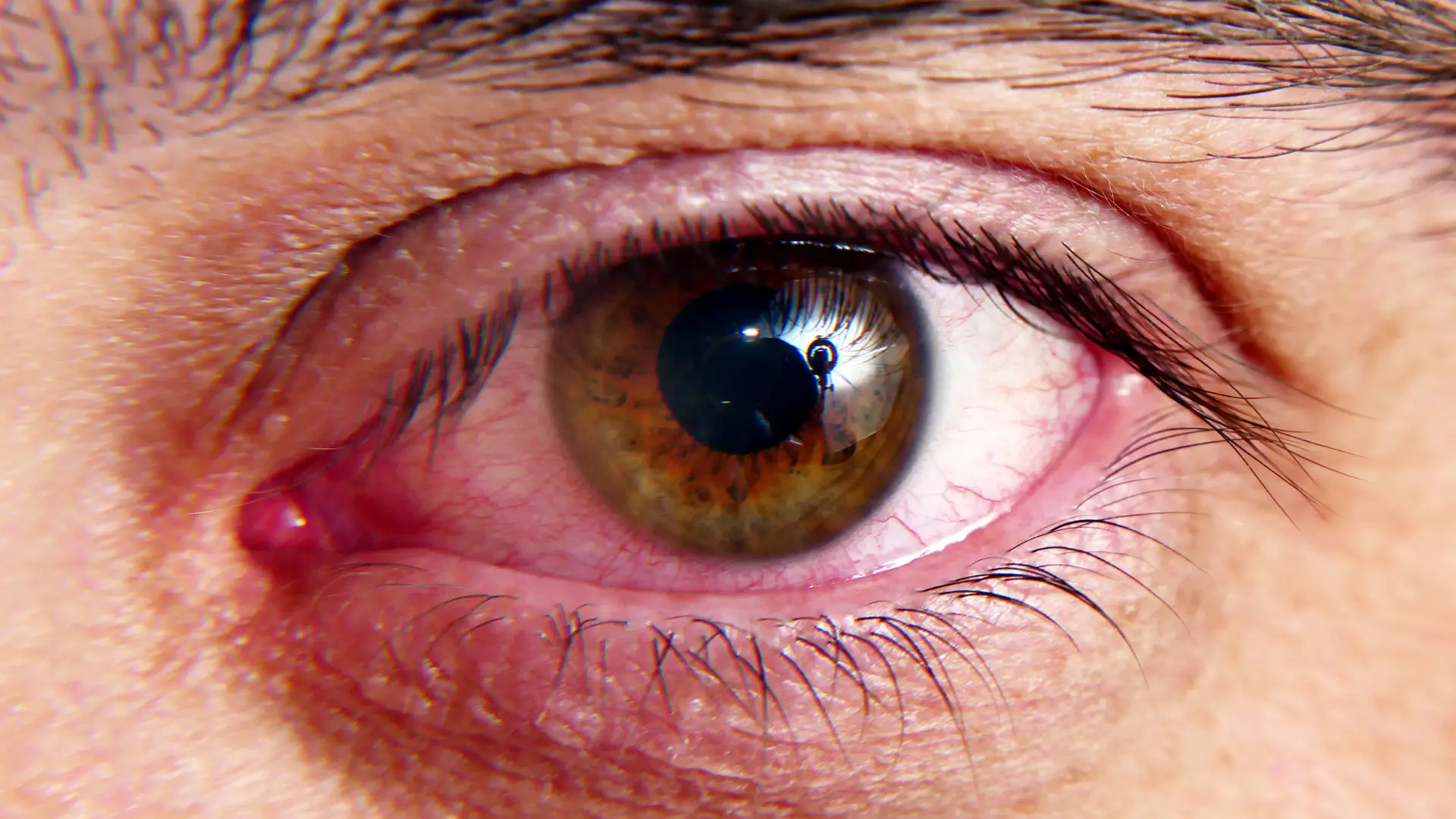
Allergic reactions to bimatoprost eye drops—the active ingredient in Lumigan—can range from mild symptoms such as eye redness, itching, and swelling to more severe reactions like facial swelling and difficulty breathing, though these cases are rare. These potential side effects may raise concerns among patients considering Lumigan for glaucoma treatment.
As a widely prescribed FDA-approved medication, Lumigan effectively lowers intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with glaucoma and ocular hypertension. However, like any medication, users must be aware of possible allergic reactions and other side effects. Seeking guidance from a healthcare provider can help determine whether Lumigan is a suitable treatment option and how to effectively manage any adverse reactions.
In this article, we will explore the allergic reactions associated with Lumigan, key risk factors, proper management strategies, and essential patient counseling for safe and effective use.
Key Takeaways on Lumigan Bimatoprost Ophthalmic Reaction Risk
- Lumigan (bimatoprost) is primarily used to lower intraocular pressure (IOP) in glaucoma patients but may cause allergic reactions, including eye redness, itching, and swelling.
- In rare cases, Lumigan can trigger severe allergic reactions, such as facial swelling or difficulty breathing, requiring immediate medical attention.
- Patients should monitor for both mild and serious symptoms and consult a healthcare provider if they experience persistent irritation or discomfort.
- Medical professionals can help manage potential Lumigan allergies and recommend alternative treatment options if needed.
About: Medica Depot is your trusted all-in-one supplier, offering a range of high-quality medical injectables and supplies. Buy Lumigan online at Medica Depot today! Whether for health professionals, plastic surgeons, dermatologists, licensed estheticians, or other specialists, we can offer genuine, brand-name products you may need. With Medica Depot, we prioritize serving you better to improve the patient’s quality of life.
Identifying Allergic Reactions to Lumigan
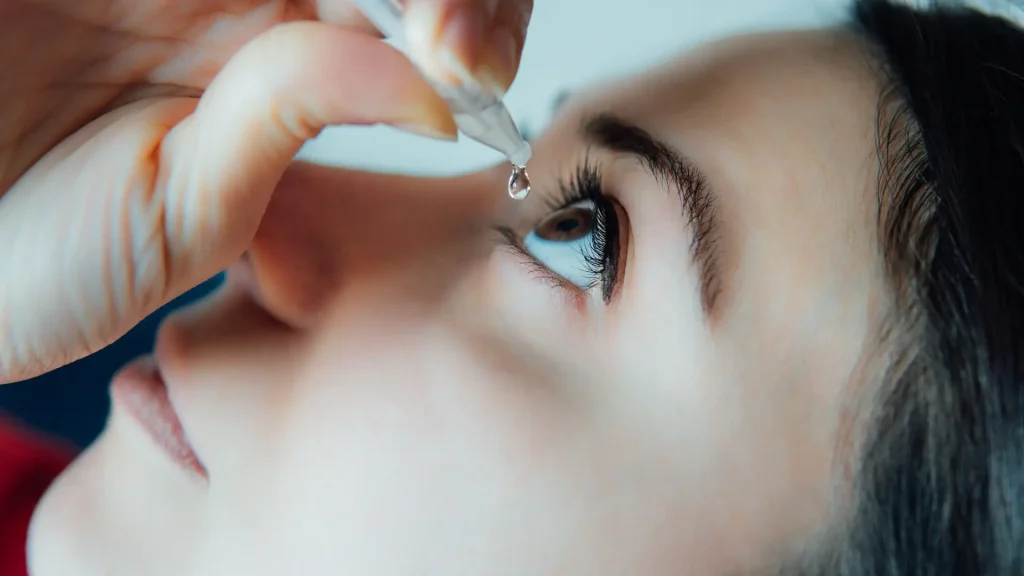

Many patients may wonder, “Why is Lumigan taken at night?” While nighttime dosing aligns with the body’s biological rhythms to optimize absorption and effectiveness in lowering intraocular pressure (IOP), it does not directly impact the likelihood of allergic reactions. However, patients should be aware of potential hypersensitivity responses when using this medication.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Lumigan 0.01% for once-daily nighttime application to manage IOP in patients with open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Despite its proven efficacy, some individuals may develop allergic reactions, requiring close monitoring and medical evaluation.
Patients experiencing allergic reactions may notice redness, itching, swelling, and discomfort in the eye, eyelid, or surrounding areas. More severe systemic reactions, such as difficulty breathing, facial swelling, or rashes, can occur shortly after application and require immediate medical attention.
Allergic Reactions vs. Side Effects
Differentiating between allergic reactions and common side effects is essential for proper management:
- Allergic reactions are immune responses that persist or worsen over time, often presenting as itching, swelling, and redness.
- Side effects, such as mild eye irritation, dryness, or changes in eyelash growth, are typically dose-dependent and may diminish with continued use.
Risk Factors for Developing Lumigan Allergies
Consulting a healthcare professional can help distinguish, determine, and appropriately manage Lumigan allergic reactions when they occur. Risk factors for developing allergies to this bimatoprost ophthalmic solution include the following:
- Patient History and Predispositions: Individuals with a known hypersensitivity to Lumigan’s ingredients—particularly prostaglandin analogs—are at a higher risk of allergic reactions. Patients with pre-existing ocular conditions, sensitivities, or a history of eye allergies may also be more susceptible.
- Concurrent Medications and Cross-reactivity: Using Lumigan alongside other ophthalmic medications can increase the risk of hypersensitivity reactions. Additionally, cross-reactivity with other prostaglandin analogs or medications containing similar active ingredients may further elevate the likelihood of developing an allergy.
Management Strategies for Lumigan-Induced Allergic Reactions

In seeking effective solutions for high eye pressure, it’s essential for patients to seek the expertise and guidance of medical professionals. Promptly consulting practitioners when symptoms occur can ensure patient safety and prevent further complications.
Steps to Take If an Allergic Reaction Occurs
- Discontinue Lumigan immediately to avoid further exposure.
- Use over-the-counter antihistamines to relieve mild symptoms, such as itching, redness, and swelling.
- Seek emergency medical care if experiencing severe symptoms, such as difficulty breathing or significant facial swelling.
If Lumigan is not well-tolerated, patients should discuss alternative options with their healthcare provider:
- Alternative Medications: Other glaucoma treatments, such as Latanoprost or Timolol, may be better tolerated and provide similar IOP-lowering benefits.
- Desensitization Protocols: In rare cases, Lumigan may be gradually reintroduced under strict medical supervision to help reduce hypersensitivity. However, this should only be attempted under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Patient Counseling on Lumigan Allergy Risks

When counseling patients about Lumigan, informing them about potential allergic reactions and adverse events is crucial. Patients should be aware of common side effects such as eye redness, itching, and increased eyelash growth or thickness.
Patients should also be informed about severe allergic reactions, such as breathing difficulties, swelling of the face, lips, or throat, and severe eye pain. Providing this information helps them recognize early signs of adverse reactions and seek timely medical attention.
A well-defined action plan enables patients to manage adverse events effectively and minimize complications. In the event of an adverse reaction, patients should follow a clear action plan:
- Immediately discontinue the use of Lumigan.
- Contact their healthcare provider.
- Seek emergency medical help for severe allergic reactions.
- Avoid touching the dropper tip to any surface, including their eyes, to prevent contamination and potential infections.
Conclusion about Lumigan Eye Treatment and Side Effects
While Lumigan is highly effective in managing intraocular pressure (IOP), patients should be aware of potential allergic reactions and their symptoms. Recognizing early warning signs allows for timely medical intervention, reducing the risk of complications and ensuring continued eye health.
Consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for patients experiencing adverse reactions, as they can provide guidance on alternative treatments and personalized management strategies. Additionally, patient education plays a key role in promoting safe medication use and optimizing treatment outcomes.
FAQs
1. What are the typical allergic reactions associated with Lumigan ophthalmic eye solution?
Common allergic reactions to Lumigan include eye redness, itching, swelling, and discomfort in the eye or surrounding areas. More severe symptoms may include difficulty breathing, facial swelling, and hives.
2. Why is Lumigan typically taken at night?
Lumigan is usually taken at night to align with the body’s biological rhythm. This can enhance the medication’s absorption, metabolism, and elimination, helping to effectively lower intraocular pressure in patients with glaucoma.
3. What should patients do if they experience an allergic reaction to Lumigan?
If patients experience an allergic reaction, stop using Lumigan immediately. Over-the-counter antihistamines may help with mild symptoms like itching and redness. For severe reactions, such as difficulty breathing, seek emergency medical care immediately.
References
- Bimatoprost Ophthalmic Solution: Package Insert / Prescribing Info. (n.d.). Drugs.com. Retrieved February 17, 2025, from https://www.drugs.com/pro/bimatoprost-ophthalmic-solution.html
- HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION LUMIGAN 0.01%. (n.d.). In AbbVie. www.rxabbvie.com. Retrieved February 17, 2025, from https://www.rxabbvie.com/pdf/lumigan_pi.pdf