Did you know that over 4 million Americans are affected by glaucoma? More than 120,000 individuals experience blindness as a result. As a leading cause of irreversible vision loss worldwide, glaucoma often develops silently, with no noticeable symptoms until significant damage has occurred.
To prevent disease progression, individuals diagnosed with glaucoma or ocular hypertension seek effective treatments to manage intraocular pressure (IOP)—the primary risk factor for optic nerve damage. Lumigan (bimatoprost ophthalmic solution) is a widely prescribed FDA-approved eye drop that helps reduce IOP by increasing the eye’s natural fluid outflow, ultimately lowering pressure and slowing disease progression.
In this article, we will explore how Lumigan effectively reduces IOP in glaucoma patients, its indications, benefits, and potential side effects, and why it remains a key treatment option for managing this sight-threatening condition.
Key Takeaways on Lumigan Bimatoprost for Glaucoma Treatment
- Lumigan eye drops (bimatoprost) effectively lower intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with glaucoma and ocular hypertension, helping to prevent optic nerve damage and vision loss.
- This medication enhances fluid outflow through two key pathways, making it a highly effective option for managing elevated IOP.
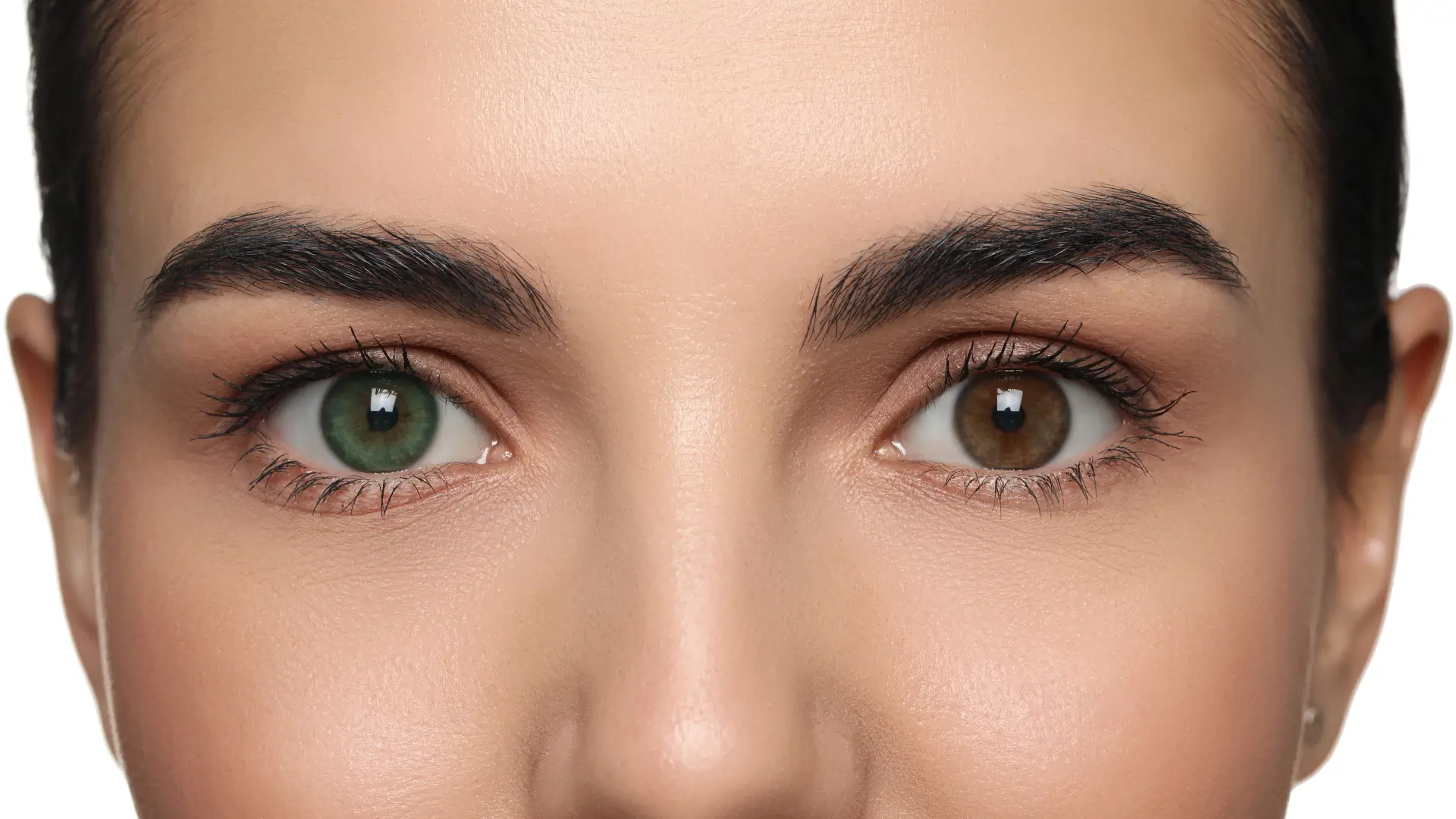
- Common side effects include eyelash growth and iris pigmentation changes, while serious adverse effects are rare but possible.
- Regular follow-ups are essential to monitor treatment progress, manage side effects, and adjust the Lumigan dosage as needed for optimal eye health results.
About: Medica Depot is your trusted all-in-one supplier, offering a range of high-quality medical injectables and supplies. Buy Lumigan wholesale at Medica Depot today! Whether for health professionals, plastic surgeons, dermatologists, licensed estheticians, or other specialists, we can offer genuine, brand-name products you may need. With Medica Depot, we prioritize serving you better to improve the patient’s quality of life.
Mechanism of Action in Lowering Intraocular Pressure
Lumigan, a US Food and Drug Administration-approved brand name for bimatoprost, has an indication to treat intraocular pressure (IOP) or high eye pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. This prostaglandin analog has a mechanism of action that enhances aqueous humor outflow.
It stands out from other treatments because Lumigan drains extra fluid in two pathways: the pressure-sensitive trabecular outflow and the pressure-insensitive uveoscleral outflow. By reducing these, Lumigan facilitates fluid drainage from the eyes, lowering IOP.
Additionally, Lumigan lowers IOP by reducing episcleral venous pressure. Its dual action mechanism makes it a compelling treatment for patients with IOP and helps prevent optic nerve damage caused by glaucoma.
Efficacy Compared to Other Treatments
Consistent use and adherence to the recommended Lumigan dosage can achieve the best therapeutic results. An observational study in a Taiwanese clinical setting showed that bimatoprost 0.01% significantly lowered intraocular pressure (IOP) in treatment-naïve patients, regardless of their initial IOP levels, as well as in previously treated patients, even those who had relatively low IOP on other therapies.
Another study comparing Lumigan vs Latanoprost demonstrated that bimatoprost significantly reduced IOP. A higher percentage reached the target IOP, with higher response rates overall. These studies underscore that Lumigan is an effective monotherapy option for treating glaucoma in IOP and ocular hypertension patients.
Additionally, Lumigan has proven beneficial as a replacement for Latanoprost, even when used alone or alongside other practitioner-prescribed medications. Bimatoprost therapy is well-tolerated and enables many patients to achieve low target pressures when it replaces latanoprost in various treatment regimens.
Patients need to seek the expertise and guidance of medical professionals to ensure they can maximize the benefits of the eye treatment with the prescribed protocol. While bimatoprost can deliver satisfactory results, the eye specialist may also recommend combination therapy for patients requiring more aggressive IOP management.
Side Effects and Contraindications
Despite the proven safety and efficacy, individuals should understand the potential risks of the treatment. According to the Lumigan prescribing information, the commonly reported adverse effects of bimatoprost include the following:
- Blepharal pigmentation
- Iris hyperpigmentation
- Eye lash changes
- Intraocular inflammation
Though less common, severe allergic reactions, macular edema, changes in iris color, and vision disturbances are possible serious adverse effects. Furthermore, patients with inflammatory eye conditions, active intraocular inflammation, or recent eye surgery should not use Lumigan. Individuals allergic to bimatoprost or any of its components must avoid using this medication.
Additionally, patients with a history of retinal detachment or certain eye infections should not use Lumigan. Pregnant or breastfeeding women must consult their healthcare provider before using Lumigan, as its safety in these populations is not established.
Patient Monitoring and Follow-Up
Medical practitioners must set regular follow-up appointments with patients to assess treatment effectiveness, address any concerns, and make necessary adjustments. This involves evaluating treatment by measuring IOP every three to six months, determining if the target IOP is maintained and the patient’s treatment response.
If the target IOP has yet to be achieved or patients experience adverse reactions, healthcare providers may adjust the Lumigan therapy. These adjustments may include changing the Lumigan dosage, switching to a different medication, or adding another treatment.
Patients must adhere to follow-up appointments and communicate any concerns or changes in their eye condition to their healthcare provider to ensure optimal glaucoma or ocular hypertension management.
Clinical Guidelines and Recommendations
It’s essential for medical professionals to follow the best practices when prescribing Lumigan treatments for patients. A thorough consultation with individuals can ensure patient suitability and product efficacy to create a tailored treatment plan and achieve optimal outcomes.
- Assess Patient History: Review the patient’s medical history, considering any previous treatments for glaucoma or ocular hypertension, allergies, and any history of inflammatory eye conditions.
- Dosage and Administration: Administer one drop in the affected eyes once daily in the evening. Do not use more than once daily, as increased frequency can reduce the intraocular pressure-lowering effect.
- Monitor for Side Effects: Monitor patients regularly for common side effects like conjunctival hyperemia, eye redness, and eye lash changes. Instruct patients to report any severe adverse effects immediately.
- Patient Education: Inform patients about the possibility of permanent iris pigmentation. Also, doctors should also emphasize the importance of sticking to the valid prescription of the treatment regimen.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Schedule regular follow-up appointments to evaluate the treatment’s effectiveness and make any necessary adjustments to the therapy.
Conclusion
Lumigan eye drops effectively reduce intraocular pressure in individuals with glaucoma or ocular hypertension. By enhancing fluid outflow from the eyes, this medication helps to protect the optic nerve and prevent vision loss. Patients responding well to Lumigan often experience improved condition management, making it a viable option in treatment plans.
However, patients must remain vigilant about potential side effects and maintain regular communication with their healthcare providers. Proper usage, adherence to follow-up appointments, and adjustments to treatment, if necessary, are key to achieving optimal results in managing glaucoma and eye health.
FAQs
1. What is Lumigan used for?
Lumigan eye drops containing bimatoprost are prescribed to lower intraocular pressure (IOP) or high eye pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. These eye drops help prevent optic nerve damage.
2. What are the common side effects of Lumigan?
Common side effects include changes in eye lash appearance, iris pigmentation, and possible intraocular inflammation. Serious side effects like allergic reactions and eye vision disturbances can occur, but are less common.
3. How should patients manage their treatment with Lumigan?
Patients should adhere to their prescribed eye dosage and attend regular follow-up appointments to assess the effectiveness of the treatment. Notifying healthcare providers of side effects or concerns is crucial for optimal glaucoma eye treatment.
References
- Glaucoma Facts And Stats – Glaucoma Research Foundation. (n.d.). Glaucoma Research Foundation. Retrieved February 13, 2025, from https://glaucoma.org/articles/glaucoma-facts-and-stats
- Simmons, S. T., Dirks, M. S., & Noecker, R. J. (2004). Bimatoprost versus latanoprost in lowering intraocular pressure in glaucoma and ocular hypertension: results from parallel-group comparison trials. Advances in therapy, 21(4), 247–262. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02850157