A clinical trial found that once-daily bimatoprost was more effective in lowering sustained intraocular pressure (IOP) than twice-daily timolol, with significant improvements over four years and no major safety concerns. This highlights bimatoprost’s long-term efficacy and tolerability as a trusted treatment for glaucoma and ocular hypertension.
One of the most widely recognized formulations of bimatoprost is Lumigan, a prescription eye drop designed to increase fluid outflow from the eye, effectively reducing IOP and preventing potential vision loss.
This article will explore Lumigan’s generic name, bimatoprost, including its uses, clinical benefits, comparisons with other treatments, and regulatory approvals, helping patients and healthcare providers better understand this essential medication.
Key Takeaways on Lumigan (Bimatoprost) For Eye Health
- Bimatoprost (sold as Lumigan) effectively lowers intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension by increasing fluid outflow from the eye.
- Beyond its primary use, Lumigan is sometimes prescribed off-label to enhance eyelash growth in individuals with hypotrichosis.
- A single daily dose provides IOP reduction for at least 24 hours, making it a convenient and effective treatment option.
- While generally well-tolerated, Lumigan may cause side effects such as eye redness and pigmentation changes, emphasizing the need for patient awareness and regular consultations with a healthcare provider.
About: Medica Depot is your trusted all-in-one supplier, offering a range of high-quality medical injectables and supplies. Order Lumigan online at Medica Depot today! Whether for health professionals, plastic surgeons, dermatologists, licensed estheticians, or other specialists, we can offer genuine, brand-name products you may need. With Medica Depot, we prioritize serving you better to improve the patient’s quality of life.
Pharmacodynamics and Mechanism of Action
According to Drugbank Online, bimatoprost is a prostaglandin analog used to treat hypotrichosis of the eyelashes and reduce intraocular pressure in open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. The US Food and Drug Administration has approved bimatoprost under the brand names Latisse and Lumigan to treat these conditions.
Bimatoprost lowers intraocular pressure (IOP) by increasing the outflow of aqueous humor through both the trabecular meshwork and uveoscleral pathways. This dual mechanism effectively reduces IOP, delivering optimal treatment outcomes to patients.
Indications and Usage
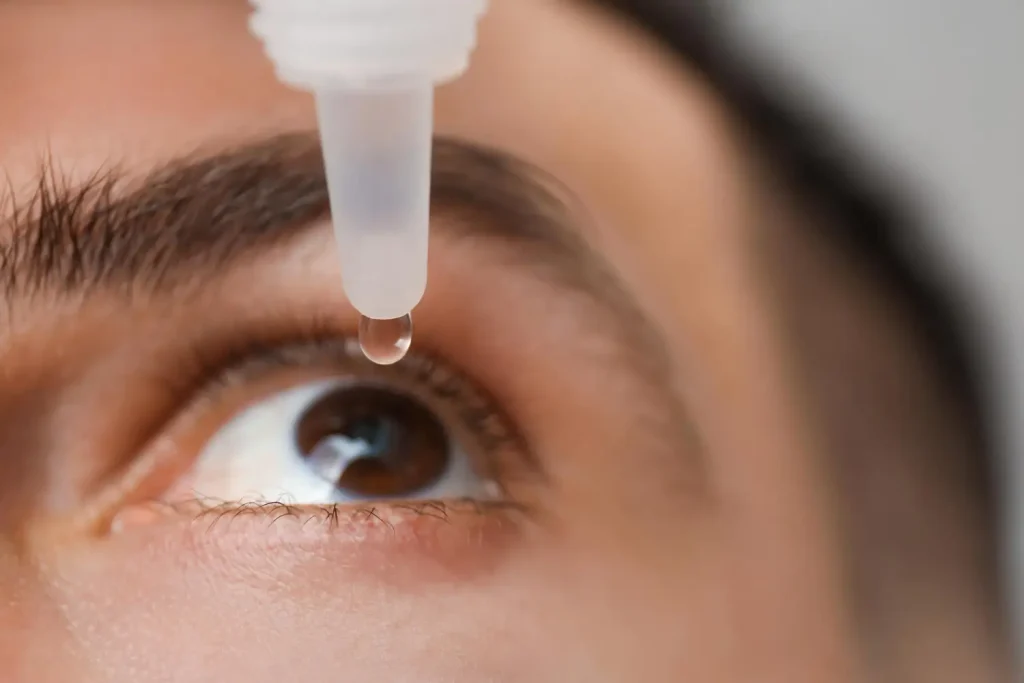
Lumigan helps prevent vision loss by enhancing fluid drainage from the eye. In particular, this ophthalmic solution has indications and uses for reducing elevated intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension.
Although not officially approved for these uses, Lumigan is also occasionally prescribed off-label to promote eyelash growth in individuals with hypotrichosis or inadequate or insufficient eyelashes.
Comparison with Other Prostaglandin Analogs

Practitioners and individuals should understand the differences between Lumigan vs Latanoprost, Travoprost, or other prostaglandin analogs when comparing these treatments. While they can lower intraocular pressure (IOP), a comparison study has shown that Lumigan (bimatoprost) has proven more effective than the timolol and latanoprost combination. It provides a potent alternative to patients with IOP.
However, practitioners and individuals should take note that potential Lumigan side effects may occur. Bimatoprost often leads to common adverse reactions, such as conjunctival hyperemia or eye redness, eyelash growth, and pigmentation changes. Some patients may also have rare and severe reactions, requiring prompt consultation with medical practitioners and appropriate management of symptoms.
Consistent application and patient education are key to maximizing Lumigan’s effectiveness. Healthcare providers should ensure patients understand its safety, efficacy, and unique pharmacological properties to achieve the best results.
Below are the key properties of Lumigan or bimatoprost:
- Mechanism of Action: Bimatoprost is a synthetic structural analog of prostaglandin F2-alpha and prostaglandin E2. It lowers intraocular pressure (IOP) by enhancing aqueous humor outflow through both the trabecular meshwork and uveoscleral pathways.
- Long-Lasting Effects: A single daily dose provides a sustained IOP reduction for at least 24 hours, making Lumigan a highly effective and convenient treatment requiring only once-daily application.
- Dual Receptor Activity: Bimatoprost acts on both prostaglandin F2-alpha and prostaglandin E2 receptors, which may further enhance its IOP-lowering effects.
Regulatory Approvals and Formulations For A Healthcare Provider To Thoroughly Understand

- US Food and Drug Administration: On March 16, 2001, the US FDA approved Lumigan (bimatoprost) ophthalmic solution to reduce elevated intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension.
- International Approvals: Lumigan is approved for use in multiple countries outside the United States, including the European Union, for the same indications.
The manufacturer effectively developed two concentrations for Lumigan, including 0.01% and 0.03%. The concentration mainly depends on the practitioner’s recommendations based on the patient’s condition, overall health, and individual needs. Patients must administer the medication as eye drops, applying one drop to the affected eye(s) once daily in the evening.
Cost Considerations: Brand vs. Generic
Currently, Lumigan does not have a therapeutically equivalent generic version available in the United States. The U.S. FDA has only approved Careprost, a generic version of Latisse, for treating hypotrichosis (insufficient eyelash growth), but not as a substitute for Lumigan in glaucoma or ocular hypertension treatment.
Cost and Insurance Coverage
- A 3mL bottle of Lumigan ranges from $35 to $60, depending on the pharmacy or supplier.
- Health insurance generally covers Lumigan when prescribed for medical conditions such as glaucoma or ocular hypertension.
- Generic versions of prostaglandin analogs are typically covered, but insurance rarely includes coverage for cosmetic uses, such as eyelash growth treatments.
Conclusion
With its active ingredient, bimatoprost, Lumigan is a highly effective treatment for managing elevated intraocular pressure in open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Its dual mechanism of action provides consistent IOP reduction, helping to prevent vision loss with once-daily use. Additionally, its off-label application for eyelash growth highlights its versatility in ophthalmic care.
However, as with any medication, understanding potential side effects and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers is essential for safe and effective treatment. By being well-informed about benefits and risks, individuals can make confident decisions that best support their eye health and overall well-being.
FAQs
1. What is Lumigan used for?
Lumigan is primarily used to lower elevated intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension, helping to prevent vision loss.
2. How does bimatoprost work in reducing intraocular pressure?
Bimatoprost lowers intraocular pressure by enhancing the outflow of aqueous humor through two pathways: the trabecular meshwork and uveoscleral routes. This effectively manages conditions like glaucoma and ocular hypertension.
3. How does Lumigan compare to other prostaglandin analogs like Latanoprost?
Lumigan (bimatoprost) is often more effective than Latanoprost and Travoprost at reducing intraocular pressure (IOP) and typically requires just once-daily dosing. While it shares common side effects—like eye redness and eyelash pigmentation changes—patients should consult their healthcare provider to find the best treatment option.
References
- Williams, R. D., Cohen, J. S., Gross, R. L., Liu, C. C., Safyan, E., Batoosingh, A. L., & Bimatoprost Study Group (2008). Long-term efficacy and safety of bimatoprost for intraocular pressure lowering in glaucoma and ocular hypertension: year 4. The British journal of ophthalmology, 92(10), 1387–1392. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjo.2007.128454
- Oddone, F., Manni, G., Parravano, M., Cupo, G., Costa, G., & Bucci, M. G. (2003). Six-Months Comparison of the Efficacy and Safety of Bimatoprost 0.03% Versus the Association of Timolol 0.5% and Latanoprost 0.005%. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, 44(13), 4344–4344. https://iovs.arvojournals.org/article.aspx?articleid=2416143