For medical professionals, the quality and safety of medical devices are always a high priority. When it comes to choosing the right products, CE-marked medical devices stand out due to their stringent regulatory requirements. This article explores why CE marked medical devices are a smart choice, detailing the benefits of CE marking and highlighting some key products that have earned this certification. It also follows our previous article detailing how medical devices are regulated in Europe.
Key Takeaways
- CE-marked medical devices meet strict European standards for safety and efficacy.
- CE marking involves rigorous testing and compliance with EU regulations.
- Dermal fillers and botulinum toxins that are CE-marked offer high quality and reliability.
- Market access across the European Economic Area (EEA) is more easily facilitated with CE marking.
What is a CE Mark?
The CE mark is a symbol that indicates a product complies with European Union (EU) safety, health, and environmental protection standards. For medical devices, achieving CE marking means the product has met rigorous testing and regulatory requirements. This ensures that It is safe and effective for patient use. This certification is essential for market access within the EU and the broader European Economic Area (EEA).
Key Benefits of CE Marking
- Rigorous testing and compliance: CE marking requires comprehensive testing and compliance with EU regulations, ensuring high standards of safety and efficacy.
- Market access: CE-marked products can be sold freely across the EEA, providing manufacturers with a wide market reach.
- Consumer confidence: The CE mark is recognized as a symbol of quality and safety, instilling confidence in both healthcare professionals and patients.
The CE Marking Process
Achieving CE marking for a medical device involves multiple steps to ensure the product meets stringent safety and performance standards. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- Identify applicable directives: Determine which EU directives apply to the medical device.
- Risk classification: Classify the device based on risk categories (Class I, IIa, IIb, III).
- Select conformity assessment route: Choose the appropriate assessment route according to the device classification.
- Prepare technical documentation: Develop comprehensive documentation covering design, manufacturing processes, and intended use.
- Conduct clinical evaluation: Gather evidence on the device’s safety and performance through clinical studies.
- Notified body review: For higher-risk devices, submit documentation to a notified body for review and certification.
- Declaration of conformity: Formally declare that the device meets all relevant EU requirements.
- Affix CE mark: Apply the CE mark to the device and its packaging, including the notified body’s identification number if necessary.
- Register the device: Register with the appropriate competent authorities in the EU.
- Post-market surveillance: Implement a system for ongoing monitoring and reporting of the device’s performance and safety.
Why CE Marked Medical Devices Are a Good Choice
The primary reason to choose CE marked medical devices is the assurance of safety and efficacy. The rigorous testing and evaluation required for CE marking ensure that these devices meet high standards, reducing the risk of complications and helping to improve patient outcomes.
Safety and Efficacy from a Comprehensive Regulatory Framework
The CE mark medical device requirements are part of a comprehensive regulatory framework designed to protect patients and healthcare providers. This framework includes the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which imposes strict guidelines on device classification, clinical evaluation, and post-market surveillance.
Quality Assurance
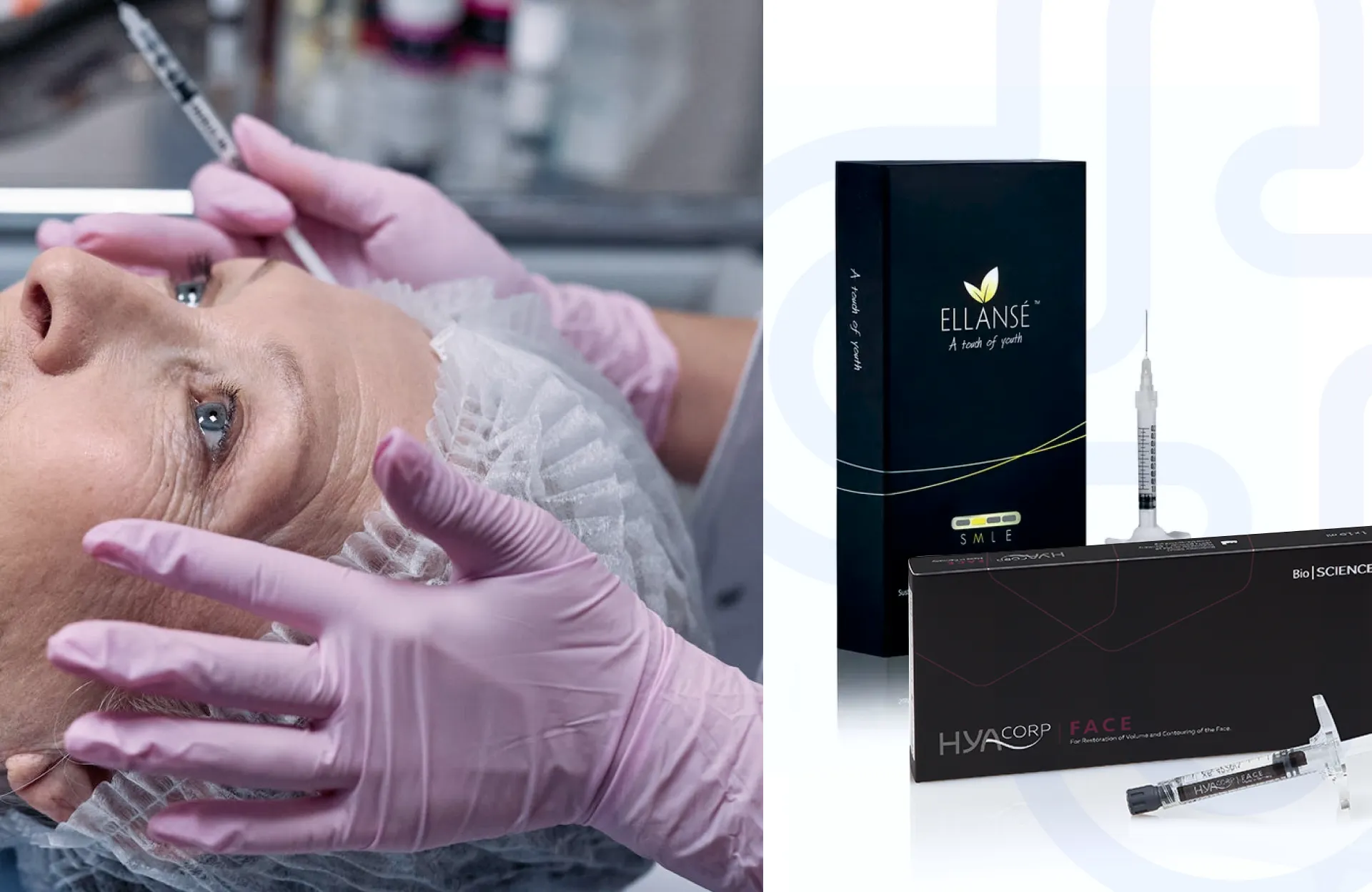
CE marking is a testament to the quality of a medical device. Products that achieve this certification have undergone extensive testing and meet stringent quality standards. This is particularly important for devices like dermal fillers and botulinum toxins, where both safety and effectiveness are critical.
Wide Range of CE Marked Products
A variety of top-tier medical products have achieved CE marking, demonstrating their adherence to rigorous European standards:
- Stylage: Celebrated for its innovative dermal fillers in aesthetic treatments.
- Teosyal: Famous for its hyaluronic acid-based dermal fillers.
- Ellansé: Provides dermal fillers with distinctive properties for prolonged results.
- Hyacorp: Specializes in premium dermal fillers for facial and body contouring.
- Perfectha: Offers a range of hyaluronic acid fillers for diverse aesthetic needs.
- Botulax: A CE-marked botulinum toxin, presenting an alternative to FDA-approved products.
Global Recognition
While CE marking is primarily an EU certification, it is often recognized and respected in countries outside of the EU. This wider recognition can facilitate the acceptance of CE marked devices in other markets, providing manufacturers with broader market opportunities.
Post-market Surveillance and Vigilance
This is an essential aspect of the CE marking process. This involves continuous monitoring of the device’s performance and safety once it is on the market. Manufacturers must implement vigilance systems to track and report any adverse events or incidents related to their devices. This proactive approach helps maintain high safety standards and ensures prompt action if any issues arise.
The Role of Notified Bodies
Notified bodies play a key role in the CE marking process for higher-risk devices. These independent organizations are designated by EU countries to assess the conformity of certain products before they can be placed on the market. They review the technical documentation, conduct audits, and issue certifications. Their involvement ensures that the device meets all regulatory requirements and is safe for use.
Compliance with EU MDR
The Medical Device Regulation (MDR) introduced in 2017 and fully implemented in May 2021, brought significant changes to the regulatory framework. The MDR replaces the previous Medical Device Directive (MDD) and introduces stricter requirements for clinical evaluation, post-market surveillance, and device classification. Achieving MDR compliance requires manufacturers to adapt their processes and documentation to meet these new standards, ensuring a higher level of safety and efficacy for medical devices.
Choosing CE-marked medical devices is a smart decision for healthcare professionals looking for high-quality, safe, and effective products. The rigorous testing and regulatory requirements behind the CE mark ensure that these devices meet the highest standards, providing confidence in their use and reliability. By opting for CE-marked products, medical professionals can enhance patient outcomes and contribute to the overall quality of care.
For detailed information and to explore our selection of CE-marked medical devices, schedule a meeting with our sales team.
FAQ
What is a CE-certified medical product?
A CE certified medical product is one that has met the safety, health, and environmental protection standards required by the European Union.
What does CE on a device mean?
CE on a device indicates that the product complies with EU regulations and has been deemed safe and effective for use.
What is the difference between CE mark and 510k?
The CE mark is a European certification, while 510(k) is a pre-market submission to the FDA in the United States. Both signify that a product meets regulatory standards, but they follow different processes and requirements.
Is CE better than the FDA?
Neither is inherently better – they are different regulatory systems with their own standards and processes. Both aim to ensure product safety and efficacy.
Do CE marks expire?
CE marks do not expire, but ongoing compliance with regulatory requirements and periodic re-certification may be necessary, especially under the new MDR regulations.
References
- French-Mowat, E., & Burnett, J. “How are medical devices regulated in the European Union?” J R Soc Med. 2012 Apr; 105(Suppl 1): S22–S28. doi: 10.1258/jrsm.2012.120036. PMCID: PMC3326593.
- Medical devices | European Medicines Agency. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory-overview/medical-devices