Millions of adults worldwide are actively trying to lose weight—and many struggle to do it with lifestyle changes alone. During and after the COVID‑19 pandemic, demand for medical weight-loss options has grown rapidly. To meet this need, once-weekly injectable medications like Wegovy and Mounjaro have emerged as powerful, guideline-supported tools.
Wegovy contains semaglutide, a GLP‑1 receptor agonist approved for chronic weight management. Mounjaro, branded for type 2 diabetes, delivers tirzepatide—a dual GIP/GLP‑1 receptor agonist also approved for weight loss under Zepbound. Both treatments offer convenience, strong clinical results, and increasing real-world success for patients with obesity or excess weight.
In this article, we compare Mounjaro and Wegovy by their mechanisms, weight-loss outcomes, side effects, dosing, cost, and prescribing tips. Whether you’re a clinician or patient, this guide will help you choose the injectable therapy that fits your needs best.
Key Takeaways
- Mounjaro (tirzepatide) and Wegovy (semaglutide 2.4 mg) are once-weekly injectable medications approved for weight management, but they work through different mechanisms and have distinct indications.
- Mounjaro acts on both GIP and GLP‑1 receptors, while Wegovy targets only the GLP‑1 pathway. This dual activity may result in greater weight reduction for some patients.
- In clinical trials, tirzepatide achieved 15–21% average weight loss over 72 weeks, compared to 10–15% with semaglutide. Effectiveness can vary depending on patient profile and comorbidities.
- Both drugs share common side effects, including nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort, but discontinuation due to these effects remains in the low- to mid-single-digit range.
- Proper training, titration schedules, and patient counseling, are all critical for safe administration and long-term treatment success.
- Healthcare providers should individualize treatment choices based on weight-loss goals, glycemic needs, access, and tolerability, while monitoring for rare but serious risks like pancreatitis and thyroid-related concerns.
About: Medica Depot is your trusted all-in-one supplier, offering a range of high-quality medical injectables and supplies. If you’re looking to buy Mounjaro, contact Medica Depot’s sales representatives and they will guide you on how to do so. Whether for health professionals, plastic surgeons, dermatologists, licensed estheticians, or other specialists, we can offer genuine, brand-name products you may need. With Medica Depot, we prioritize serving you better to improve the patient’s quality of life.
How Mounjaro’s Dual Mechanism Differs from Wegovy
Before starting any weight-loss therapy, patients benefit from speaking with a qualified medical provider. Adults exploring non-surgical pharmacologic weight-management therapies should ask about the differences between tirzepatide and semaglutide. These injectable options are often compared for their safety, effectiveness, and real-world outcomes.
When discussing Mounjaro vs Wegovy, understanding their mechanisms of action is important. This knowledge helps patients make informed decisions based on how each medication works in the body.
- Mounjaro (Tirzepatide): A dual GIP and GLP‑1 receptor agonist. It increases glucose-dependent insulin secretion, reduces glucagon, slows gastric emptying, and helps suppress appetite.
- Wegovy (Semaglutide): A selective GLP‑1 receptor agonist. It also slows gastric emptying and reduces appetite through central pathways.
Both are FDA-approved but for different uses: tirzepatide is marketed as Mounjaro for type 2 diabetes and Zepbound for chronic weight management, while semaglutide 2.4 mg (Wegovy) is approved for chronic weight management. Wegovy also reduces the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events in adults with obesity or overweight and existing cardiovascular disease.
Clinical Trial Evidence on Mounjaro vs Wegovy

Both Mounjaro (tirzepatide) and Wegovy (semaglutide) have been evaluated in large, rigorous clinical trials that demonstrated their ability to produce significant weight loss and improve overall health outcomes. Reviewing these studies helps providers choose the most appropriate therapy for each patient.
The SURMOUNT-1 trial investigated tirzepatide in adults with obesity but without diabetes. At 72 weeks, participants achieved an average 15–21% reduction in body weight, depending on the dose. These results marked one of the most substantial effects seen in an anti-obesity drug to date.
In SURMOUNT-2, which focused on patients with type 2 diabetes, the weight loss was more modest yet still clinically meaningful, averaging 12–15% of baseline body weight. Importantly, patients also saw improvements in blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and lipid profiles, highlighting broader health benefits beyond weight reduction.
The STEP trial program established semaglutide 2.4 mg as an effective long-term treatment for weight loss and obesity care. In STEP 1, adults without diabetes experienced an average 14.9% reduction in body weight at week 68 compared to placebo.
Extended results from STEP 5 showed that participants maintained a 15.3% weight reduction at 104 weeks, reinforcing the drug’s durability in supporting long-term health improvements. These findings positioned Wegovy as a reliable therapy for chronic weight management.
Comparative Insights for Clinical Care
Head-to-head analyses suggest that Mounjaro produces greater average weight loss than Wegovy, with reductions up to 20% compared to 15% for semaglutide in comparable populations. Both drugs share a similar profile of gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea, constipation, and diarrhea, which are typically manageable with proper counseling.
When choosing between the two, clinicians should consider body weight goals, blood sugar targets, comorbid health conditions, and patient access to therapy. Ongoing monitoring and comprehensive care remain essential to maximize the benefits of either treatment.
Comparing Side Effects and Tolerability Between Mounjaro and Wegovy
Even with FDA approval, both drugs carry potential risks. Reviewing their prescribing information and clinical trials helps clarify what patients might experience during treatment.
Mounjaro’s commonly reported side effects include:
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Decreased appetite
- Vomiting
- Constipation
- Dyspepsia
- Abdominal pain
Wegovy’s side effects are broader and include the following:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Abdominal pain
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Indigestion
- Flatulence
- Reflux symptoms
- Nasopharyngitis
- Hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes
Serious risks—while uncommon—may involve cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, acute pancreatitis, kidney injury from dehydration, and hypoglycemia, particularly when combined with insulin or sulfonylureas.
Discontinuations due to gastrointestinal effects are generally in the low- to mid-single digits for both therapies and increase with dose. Rates vary depending on the trial population, so clinicians should refer to individual studies or the drug labels for specifics.
Practical Considerations for Prescribing Mounjaro or Wegovy
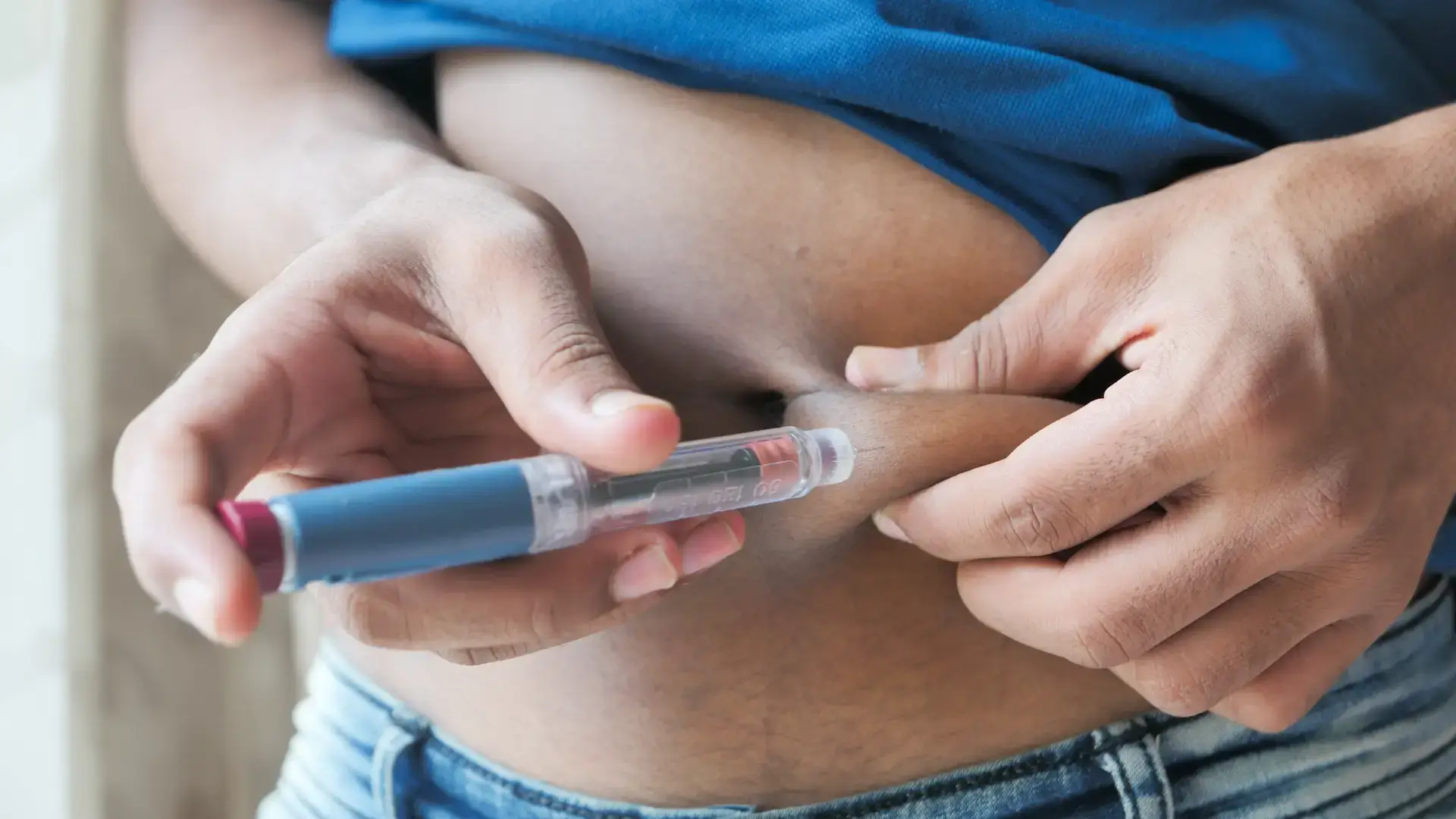

Prescribers must understand the differences and similarities between Mounjaro (tirzepatide) and Wegovy (semaglutide) when selecting therapy for patients seeking significant weight loss and improved metabolic health. Both drugs are administered once weekly as a subcutaneous injection into the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm. Patients should rotate sites and avoid injecting into tender, bruised, or red areas.
Prescribers must be trained on Mounjaro injection sites and Wegovy administration. Moreover, the dosing and titration for these medications involve:
- Mounjaro: The recommended starting dose is 2.5 mg once weekly. The dose increases in 2.5 mg increments every four weeks until reaching a maximum of 15 mg. This gradual titration helps reduce gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea, diarrhea, and constipation.
- Wegovy: Treatment begins at 0.25 mg once weekly. The dose is increased every four weeks through five escalation steps until the maintenance dose of 2.4 mg weekly is achieved. This slow titration schedule supports tolerability while targeting meaningful body weight reduction.
Both Mounjaro and Wegovy carry an FDA boxed warning for thyroid C-cell tumors, observed in rodent studies. While the relevance to humans remains uncertain, these medications should not be prescribed to patients with a personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) or multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2). Clinicians should also review medical history for pancreatitis, gallbladder disease, or gastrointestinal disorders before initiating therapy.
Clinical Outcomes and Patient Care
Research from pivotal clinical trials demonstrates that both drugs can produce significant weight loss in people with type 2 diabetes or obesity. In addition to reductions in body weight, patients may experience improvements in blood sugar control, cardiovascular risk factors, and overall health.
Effective care requires individualized counseling, including dietary support, physical activity guidance, and ongoing monitoring of tolerability. By tailoring therapy and providing structured follow-up, prescribers can maximize treatment benefits while ensuring long-term adherence.
Conclusion
Mounjaro and Wegovy both offer effective options for people seeking injectable weight-loss treatments. While tirzepatide may deliver greater weight reduction due to its dual GIP/GLP‑1 activity, semaglutide has also shown strong long-term results and cardiovascular benefits.
Both therapies share similar side effect profiles, mainly involving gastrointestinal symptoms. Choosing between them depends on the individual’s health status, treatment goals, and medication access. With proper training, monitoring, and support, clinicians can guide patients toward successful outcomes.
FAQs
1. What are the main differences between Mounjaro and Wegovy?
Mounjaro activates GIP and GLP‑1 receptors; Wegovy activates GLP‑1 only. They also have different FDA-approved uses: Mounjaro (type 2 diabetes), Zepbound (weight management), and Wegovy (weight management).
2. How effective are Mounjaro and Wegovy for weight loss?
In trials, tirzepatide led to 15–21% weight loss at 72 weeks. Semaglutide 2.4 mg resulted in 10–15% weight loss, depending on the study.
3. What side effects should patients expect from Mounjaro and Wegovy?
Both medications may cause nausea, diarrhea, and other gastrointestinal effects. Discontinuation rates are generally low, and vary by dose and patient population.
References
Bailey P, Purcell S, Calvar J, Baverstock A. 45% of people globally are currently trying to lose weight. Ipsos. https://www.ipsos.com/en/global-weight-and-actions. Published January 19, 2021.
novoMEDLINK. Chronic Weight Results | Wegovy® (semaglutide) injection 2.4 mg. novoMEDLINK. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.novomedlink.com/obesity/products/treatments/wegovy/efficacy-safety/chronic-weight-management.html