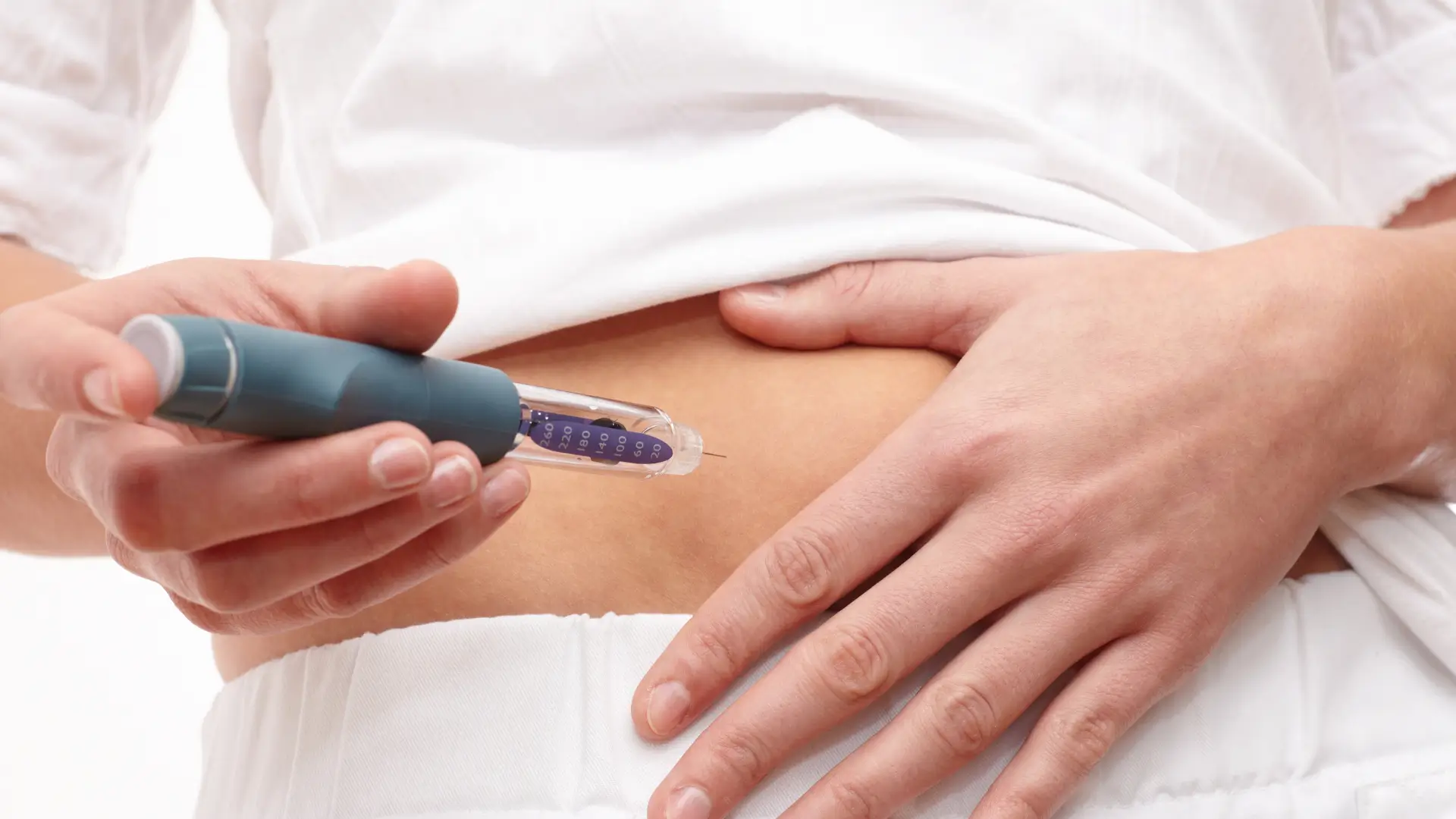
Since its approval, Mounjaro (tirzepatide) has gained attention not only for its powerful blood sugar and weight-lowering effects, but also for its side effect profile — particularly when it comes to gastrointestinal symptoms. Like many medications in the GLP-1 and GIP receptor agonist class, it commonly causes nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting, especially at higher doses. In fact, clinical trials have shown that up to 10% of patients on the highest 15 mg dose stopped treatment due to side effects.
These reactions aren’t unique to Mounjaro. Similar patterns are seen across other incretin-based injectables, where GI symptoms are most common, injection site reactions are occasional, and the risk of low blood sugar mainly occurs when used with insulin or sulfonylureas.
In this article, we’ll break down the full list of Mounjaro side effects, explore how often they occur in both studies and real-world use, and offer practical, evidence-based tips to help patients and practitioners manage them effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Mounjaro (tirzepatide) is generally well tolerated, but gastrointestinal side effects like nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting are common—especially during dose escalation.
- Serious adverse events such as pancreatitis, hypoglycemia (with insulin or sulfonylureas), and gallbladder disease are rare but clinically important.
- Starting at the recommended 2.5 mg dose and slowly titrating upward helps minimize GI discomfort and supports adherence.
- Routine monitoring of glucose levels, A1C, and weight, combined with regular follow-ups, ensures safe and sustained outcomes throughout treatment.
- Understanding and preparing for side effects allows healthcare providers to deliver more personalized, informed, and safer care.
About: Medica Depot is your trusted all-in-one supplier, offering a range of high-quality medical injectables and supplies. If you’re looking to buy Mounjaro, contact Medica Depot’s sales representatives, and they will guide you on how to do so. Whether for health professionals, plastic surgeons, dermatologists, licensed estheticians, or other specialists, we can offer genuine, brand-name products you may need. With Medica Depot, we prioritize serving you better to improve the patient’s quality of life.
Common Reactions Seen in Patients on Mounjaro: Nausea and Constipation
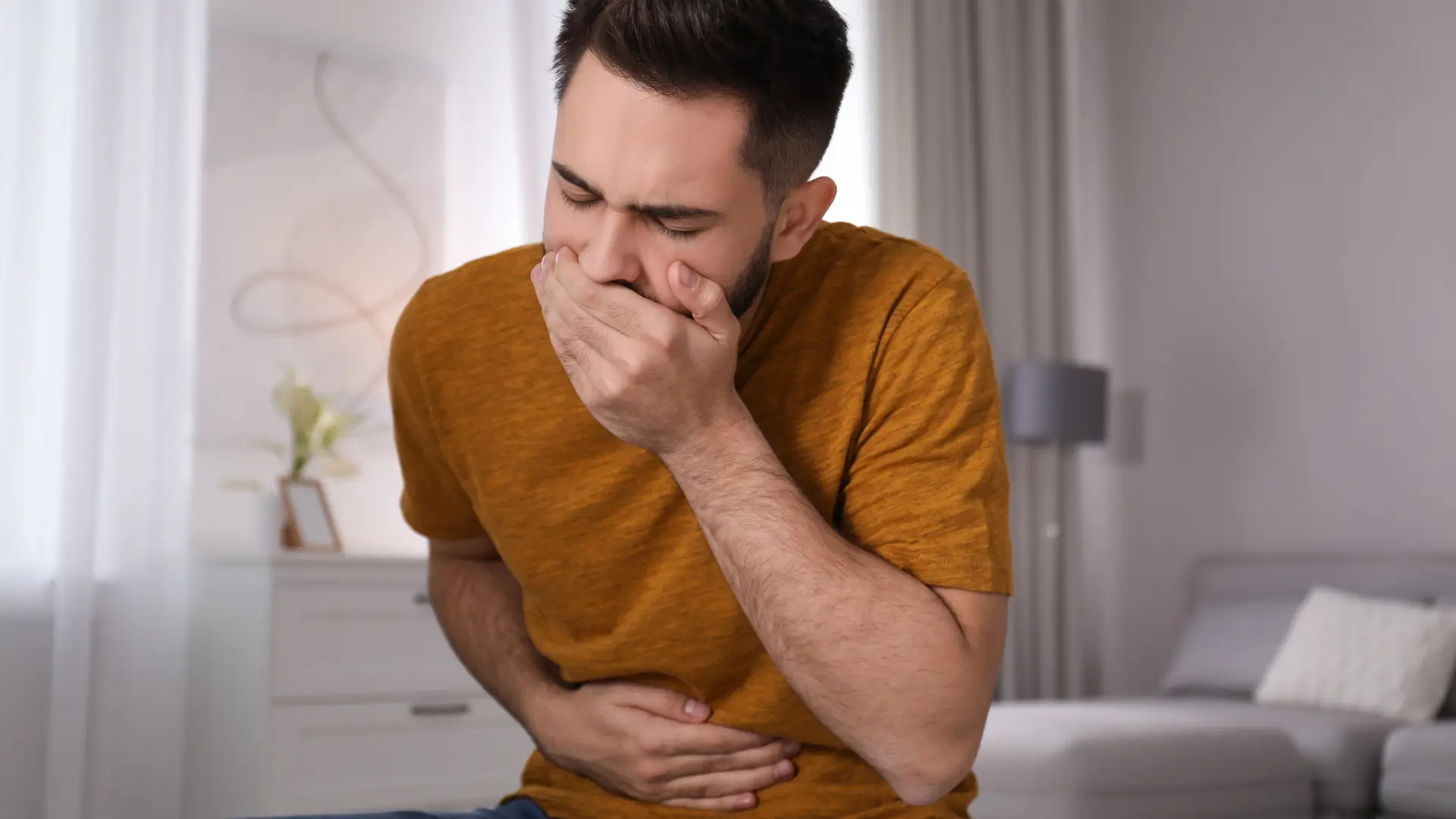

Patients considering Mounjaro for weight loss or obesity management should always seek guidance from a qualified healthcare professional. While the medication has shown strong benefits in improving blood sugar control and supporting weight loss, it can also cause side effects.
Like other medications in its class, Mounjaro can cause side effects—most of which are mild to moderate and do not usually require medical intervention.
According to clinical trial data and prescribing information, the most commonly reported effects of Mounjaro include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Decreased appetite
- Dyspepsia (indigestion)
- Abdominal pain
Gastrointestinal Reactions: Constipation and Nausea
Among the most noticeable reactions are nausea and constipation. Nausea often presents early in treatment and may improve with slower dose escalation, smaller meals, and hydration. Constipation can persist longer in some patients but is usually manageable with dietary fiber, fluid intake, and medical guidance if needed. On the other hand, some patients report diarrhea, highlighting the variable way the gut can respond.
These common side effects tend to occur during the first weeks of therapy, especially as the dose increases. Many people find that their symptoms lessen as the body adjusts to the medication. If any discomfort becomes severe or prolonged, patients should speak to their provider for appropriate care and adjustment.
Serious and Rare Adverse Events Linked to Mounjaro: Allergic Reaction or Other Medical Concerns
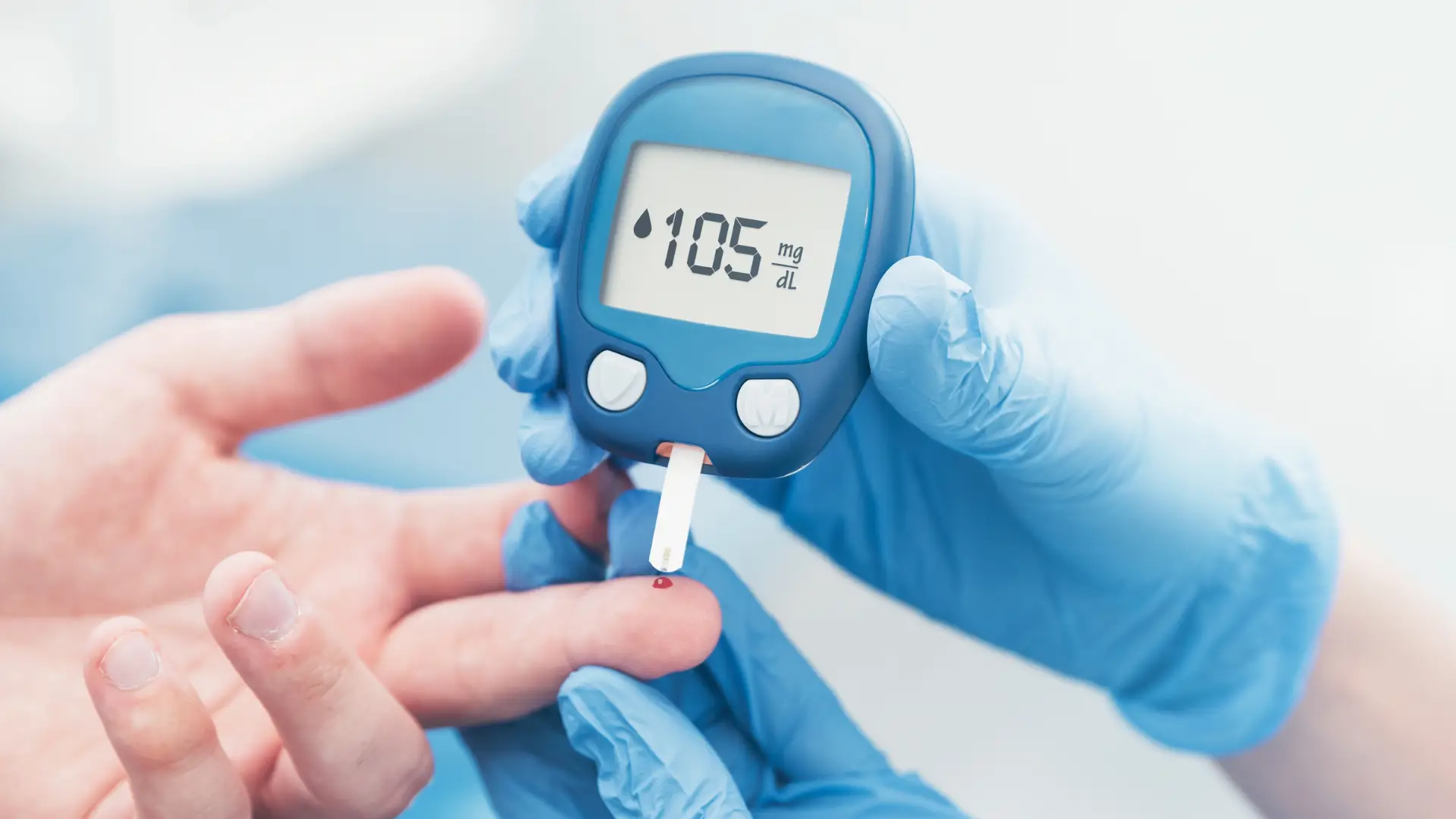
Although most patients experience only mild side effects, some rare but serious risks have been associated with Mounjaro (tirzepatide). These events highlight the importance of proper dosing, ongoing monitoring, knowing how to inject Mounjaro safely, and close collaboration with a doctor or licensed healthcare professional.
Patients may receive this medication under appropriate medical supervision, ideally in a clinic setting, or with comprehensive knowledge of self-administration. Furthermore, though infrequent, some serious risks have been linked to tirzepatide, the active ingredient in Mounjaro.
To reduce the chance of complications, practitioners should:
- Carefully screen for contraindications before prescribing
- Follow sterile injection protocols to protect patient health
- Educate patients about possible serious side effects and warning signs
Although uncommon, published trial data and post-marketing surveillance have linked Mounjaro with the following reported rare adverse events including:
- Risk of Thyroid C-cell Tumors (seen in rodents; human risk remains uncertain)
- Acute Pancreatitis
- Severe Hypoglycemia (more likely when combined with insulin or sulfonylureas)
- Hypersensitivity or Allergic Reactions
- Acute Kidney Injury related to Dehydration from Gastrointestinal Events
- Severe Gastrointestinal Reactions, such as Persistent Vomiting
- Worsening of Diabetic Retinopathy in some patients with Rapid Improvement in Blood Sugar
- Gallbladder Disease, including Gallstones
- Pulmonary Aspiration during Anesthesia, reported in Rare Postmarketing Cases
By recognizing these rare risks early, providers can better screen candidates and offer informed counseling before and during treatment.
Because practitioners use Mounjaro for both obesity and type 2 diabetes management, patients must weigh the weight loss and blood sugar benefits against these potential risks. A doctor should discuss each patient’s individual risk profile before starting therapy. By recognizing these rare complications early, providers can ensure safer outcomes and maintain long-term health.
Duration, Severity, and Management of Mounjaro Side Effects
For patients starting Mounjaro, understanding the timing, intensity, and management of potential side effects can improve treatment safety and adherence. A doctor should always guide therapy, as this medication affects both blood sugar control and weight loss outcomes.
Understanding when side effects appear, how severe they might be, and how to manage them can help clinicians support patients more effectively and improve overall treatment success.
Onset and Duration of Side Effects
- Most gastrointestinal (GI) reactions appear within the first 1–2 weeks of treatment. Common complaints include nausea, diarrhea, and reduced appetite.
- These reactions often peak during dose titration and may gradually improve by week 4 to 6, especially with a slower dose increase.
- Hypoglycemia, while not common on its own, may occur early if the patient is also taking co-medications like insulin or sulfonylureas. Monitoring helps reduce these risks.
Severity and Dose Dependence
A meta-analysis of tirzepatide trials showed the following rate of GI side effects:
- 39% at 5 mg
- 46% at 10 mg
- 49% at 15 mg
Although most reactions were mild to moderate, serious medical events—such as pancreatitis, severe hypoglycemia, or gallbladder complications—were seen in ≤1% of participants. Even though rare, these require immediate medical attention to protect long-term health.
Management Strategies
Clinicians can reduce side effects and improve tolerability with a structured approach:
- Begin with the recommended 2.5 mg Mounjaro dose once weekly for the first 4 weeks. Increase by 2.5 mg increments as tolerated.
- Encourage patients to eat smaller, bland meals and stay well-hydrated to ease GI symptoms.
- If symptoms worsen, consider holding the current dose or reducing it temporarily.
- Adjust insulin or sulfonylurea co-medications as needed to minimize hypoglycemia risk.
Long-Term Side Effects and Safety Considerations
Long-term data on Mounjaro side effects remain under review as more studies track patients over extended periods. Current findings suggest that gastrointestinal reactions are the most persistent, while severe complications remain rare. Healthcare providers monitor for possible risks such as pancreatitis or gallbladder disease, especially in patients with a history of these conditions.
Because Mounjaro is a medical treatment for both obesity and type 2 diabetes, balancing health benefits against potential risks is essential. Patients should report ongoing or severe symptoms to their provider to ensure safe and effective use.
How to Monitor and Counsel Patients Using Mounjaro
Healthcare professionals play a central role in ensuring safe and effective Mounjaro therapy. Regular monitoring of blood sugar, body weight, and potential side effects allows early intervention and better treatment outcomes. Continuous counseling also strengthens patient adherence and promotes long-term health benefits.
In the early dose titration phase, providers should arrange follow-up visits every four weeks. These visits enable a careful evaluation of tolerability and early side effects, including gastrointestinal symptoms. Once a stable maintenance dose is achieved, follow-up may be extended to every three months, provided the patient shows stable glycemic control.
At each visit, clinicians should:
- Check A1C and fasting plasma glucose to confirm effective blood sugar regulation.
- Track weight loss progress, as this is a key treatment goal for people with obesity or type 2 diabetes.
- Review injection site reactions or other medical side effects that may affect adherence.
Comparing these findings with outcomes observed in the SURPASS clinical trials provides context for deciding whether to maintain, escalate, or adjust the medication dose.
Counseling for Safe Use of Mounjaro
Proper patient education is vital in minimizing risks and maximizing results:
- Teach patients how to self-inject Mounjaro correctly, emphasizing rotation of injection sites and pen storage.
- Review the importance of taking the medication once weekly, on the same day each week.
- Explain how to recognize early signs of hypoglycemia, particularly in patients combining Mounjaro with insulin or sulfonylureas.
- Address common side effects such as nausea, constipation, or diarrhea, and provide strategies for relief.
Tools for Patient Engagement
Encouraging patients to use treatment logs or mobile health apps can improve self-management. These tools allow them to record:
- Weekly injection doses
- Daily blood glucose levels
- Episodes of side effects or discomfort
- Physical activity and dietary habits
By reviewing these logs, providers and patients can work together to adjust therapy, address concerns, and ensure continued medical safety while supporting sustainable weight loss.
Conclusion
Understanding the side effects of Mounjaro, from common symptoms like nausea to rare but serious reactions, is important for both patients and healthcare providers. With proactive monitoring, dose adjustments, and ongoing communication, most patients can successfully continue their treatment.
Though GI symptoms are the most common, they can often be managed with slow titration and supportive care. Serious adverse effects are rare but should be part of every counseling session.
Mounjaro continues to demonstrate powerful benefits in managing type 2 diabetes—especially when prescribed and monitored with care.
FAQs
1. What are the common side effects of Mounjaro?
The most frequently reported include nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal discomfort. These reactions usually emerge early and may improve over time with dose adjustment.
2. Are there serious risks associated with Mounjaro?
Risks include thyroid C-cell tumors (based on animal studies), pancreatitis, and severe GI issues. These should be discussed thoroughly with a healthcare provider.
3. How can healthcare providers help manage Mounjaro side effects?
Providers should start patients on a low dose and gradually increase it. They should also monitor blood sugar levels closely and schedule regular follow-ups to ensure effective management.
References
Mishra R, Raj R, Elshimy G, et al. Adverse Events Related to Tirzepatide. J Endocr Soc. 2023;7(4):bvad016. Published 2023 Jan 26. doi:10.1210/jendso/bvad016
Eli Lilly and Company. MOUNJARO- tirzepatide injection, solution | Eli Lilly and Company. uspl.lilly.com. Published June 2025. Accessed September 1, 2025. https://uspl.lilly.com/mounjaro/mounjaro.html#pi