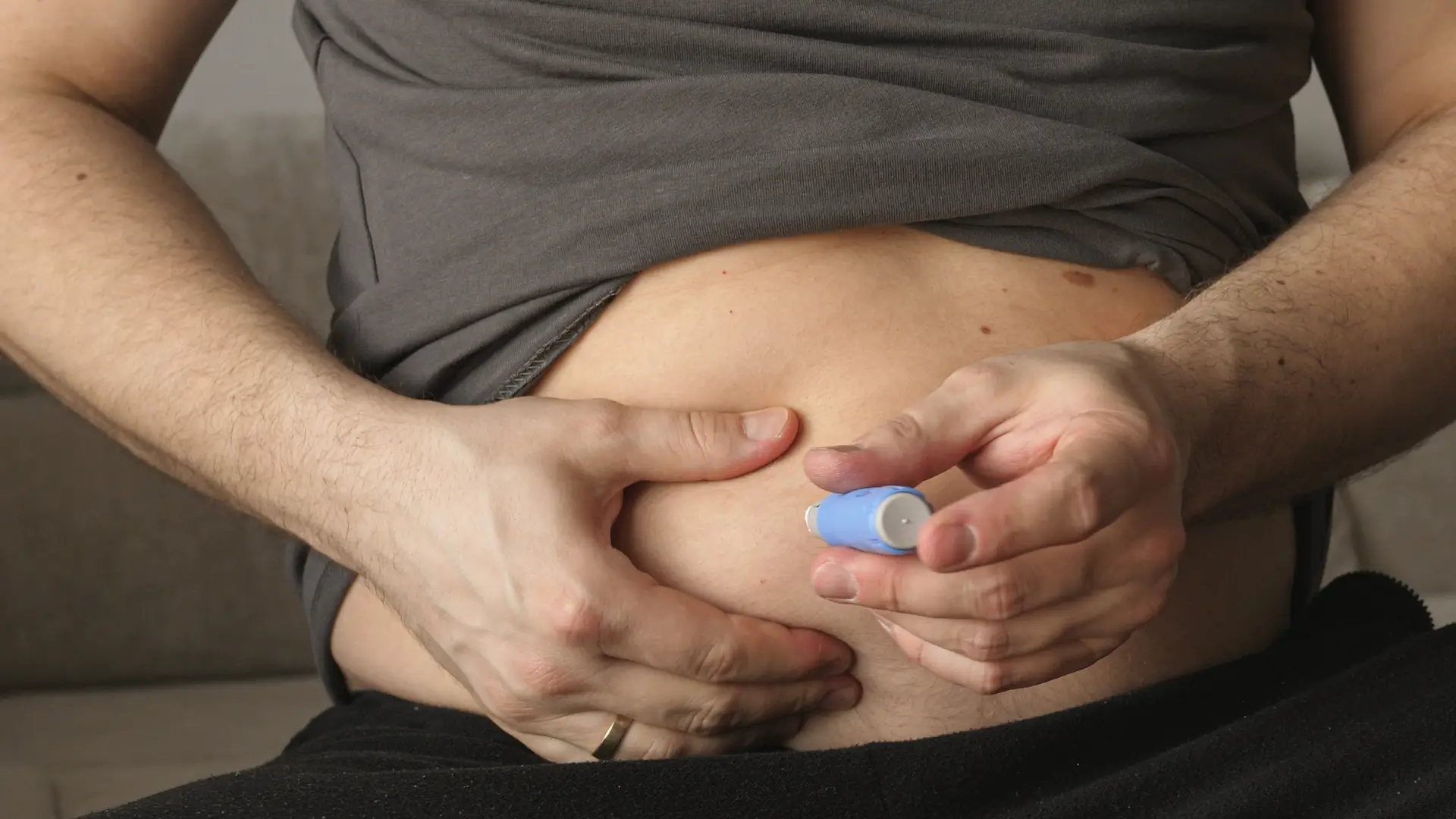
Starting Ozempic can be a game-changer for managing type 2 diabetes, but like any medication, it comes with potential side effects. For many patients, stomach-related symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea are among the first challenges they may face. These reactions are common, with over 10% of users experiencing them, as noted by regulatory agencies.
Understanding why these side effects occur and how to manage them effectively is essential for maintaining the benefits of Ozempic while minimizing discomfort. By setting realistic expectations and learning how to cope with these reactions, patients are more likely to continue their treatment and avoid unnecessary interruptions.
In this article, we’ll explore the most common side effects of Ozempic, explain when and why they may happen, offer strategies to manage them, and guide you on when to reach out to your healthcare provider for advice.
Key Takeaways about the Potential Ozempic Side Effects
- Common mild side effects of Ozempic include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain, which typically lessen over time as the body adapts.
- Serious side effects can include pancreatitis, kidney injury, and allergic reactions. Prompt medical attention is essential if these occur.
- There are long-term risks such as diabetic retinopathy complications, hypoglycemia, and gallbladder disease, which require careful monitoring.
- Gastrointestinal issues are common, especially during dose escalation. Slow titration and dietary adjustments can help reduce discomfort.
About: Medica Depot is your trusted all-in-one supplier, offering a range of high-quality medical injectables and supplies. If you’re looking to buy Ozempic, contact Medica Depot’s sales representatives and they will guide you on how to do so. Whether for health professionals, plastic surgeons, dermatologists, licensed estheticians, or other specialists, we can offer genuine, brand-name products you may need. With Medica Depot, we prioritize serving you better to improve the patient’s quality of life.
Gastrointestinal Side Effects Frequently Seen With Ozempic

Many branded medications that use GLP-1 receptor agonists in their formulations, like Saxenda vs Ozempic or Wegovy, have proven highly effective in controlling glycemic levels and aiding weight loss. For individuals looking for solutions to manage their type 2 diabetes, Ozempic offers an FDA-approved treatment for this health condition.
When patients begin taking Ozempic, they should know that this injection—used for type 2 diabetes and weight loss—may produce stomach problems and other side effects. Ozempic offers a GLP-1 receptor agonist and one of several diabetes drugs designed to help regulate blood sugar and reduce weight. Although effective, patients must remain aware of the risk of severe problems while under medical care.
- Nausea
- Stomach (abdominal) pain
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
These side effects typically appear early in treatment or during dose escalation. For most people, the symptoms lessen within a few days, especially as the body adjusts to the drug or medication. Adherence to the recommended treatment, dosing protocols, and doctor consultation can minimize common Ozempic side effects and help ensure that patients get the most out of their therapy.
Serious Adverse Events Linked to Ozempic Use (Thyroid Tumors, Kidney Disease)
While most Ozempic users experience manageable side effects, there are more serious medical events that require attention. The boxed warning on the prescribing information highlights the potential risk of thyroid C-cell tumors or thyroid cancer, making it crucial for healthcare providers to conduct thorough screening and ensure patient suitability before starting the medication.
Severe reactions linked to Ozempic pens include:
- Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas)
- Acute kidney disease or acute kidney injury may occur, especially when nausea or vomiting lead to dehydration. Patients must report stomach problems such as persistent vomiting or diarrhea.
- Severe hypersensitivity or allergic reactions
- Severe gastrointestinal intolerance
Every doctor should discuss these risks openly with patients and monitor for symptoms such as lumps in the neck, upper-right-abdominal pain, yellowing of the skin/eyes, and signs of kidney dysfunction.
Moreover, healthcare providers must avoid prescribing Ozempic to individuals with a personal or family history of MTC (medullary thyroid carcinoma) or MEN 2 (multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2), as well as those who have had serious hypersensitivity reactions to semaglutide or any of the excipients in Ozempic.
When patients experience unexpected symptoms, they must report these to their doctor immediately to ensure that the appropriate action is taken to avoid further complications.
Rare or Long-Term Risks Associated With Ozempic (Gallbladder Problems, Low Blood Sugar)
While Ozempic has shown tremendous efficacy for glycemic control and weight loss, it’s important to recognize that some rare or long-term risks could arise during treatment. For example, if not appropriately managed, side effects may lead to more serious, long-term risks:
- Diabetic retinopathy complications (eye issues)
- Hypoglycemia
- Acute gallbladder problems, including cholelithiasis or cholecystitis, have been reported in some patients taking Ozempic.
- Pulmonary aspiration during general anesthesia or deep sedation
Practitioners should counsel patients on both common and rare Ozempic side effects and ensure comprehensive screening before starting treatment. Clear communication between the healthcare provider and the patient can help manage these risks effectively and ensure safe use.
It’s also worth noting that while Ozempic has been extensively studied, evidence on long-term side effects is still being gathered. Therefore, it’s crucial to have an individualized risk assessment and keep track of any potential complications during therapy.
How Clinicians Should Monitor and Manage Ozempic Side Effects
Healthcare professionals should be well-versed in best practices to ensure Ozempic’s effectiveness and patient safety. A thorough screening process, including a review of the patient’s medical history and any potential contraindications, is essential for determining whether Ozempic is the right choice.
Here are some key steps clinicians should follow:
- Proper injection frequency and dosing: Ozempic requires a once-weekly injection with dose escalation over four weeks. Ozempic microdosing (off-label) is sometimes considered to help improve patient tolerance during therapy, though this is an unproven approach.
- Stepwise measures for gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms: Encourage slow titration; advise smaller, low-fat meals and slower eating. If nausea persists, antiemetics (medications to prevent nausea) may be considered, and dosing adjustments may be needed.
- Stop therapy and investigate severe warning signs: If serious adverse symptoms appear, discontinue Ozempic and seek immediate evaluation.
- Provide structured monitoring: Schedule regular blood glucose checks, renal function monitoring, and symptom reviews during symptomatic periods.
In cases of adverse reactions or if the Ozempic regimen isn’t working, healthcare providers may consider safer alternatives, like slower titration or switching to a different GLP-1 formulation.
Conclusion on the Risks Associated with Ozempic Pen
While Ozempic offers significant benefits for managing type 2 diabetes, its side effects – particularly gastrointestinal ones – should not be overlooked. By staying informed about these effects and managing them proactively, healthcare providers can help patients achieve optimal treatment outcomes while minimizing discomfort.
Regular follow-ups and clear patient education about the importance of proper dosing and side effect management ensure that patients feel confident and supported throughout their treatment journey. Communication between healthcare professionals and patients is key to navigating the potential challenges associated with Ozempic.
FAQs about Using Ozempic for Type 2 Diabetes
1. What are the common side effects of Ozempic?
The most common side effects from Ozempic include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain. These side effects are most commonly experienced during the first few weeks of treatment or when adjusting the dose.
2. What serious side effects should I be aware of when using Ozempic?
Serious side effects include thyroid tumors, pancreatitis, acute kidney injury, and severe allergic reactions. If you experience any unusual or severe symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
3. How can I manage the side effects of Ozempic?
Ozempic side effects, especially gastrointestinal issues, can often be managed by slow titration, adjusting diet, and using medications to control symptoms. If you continue to experience discomfort, it’s essential to talk to your healthcare provider for further guidance.
References
Patient Safety Learning. MHRA: GLP-1 receptor agonists: reminder of the potential side effects and to be aware of the potential for misuse. Patient Safety Learning: The Hub. Published October 24, 2024. Accessed October 22, 2025. https://www.pslhub.org/learn/patient-safety-in-health-and-care/medication/mhra-glp-1-receptor-agonists-reminder-of-the-potential-side-effects-and-to-be-aware-of-the-potential-for-misuse-24-october-2024-r12303/
Novo Nordisk Inc. OZEMPIC® HIGHLIGHTS of PRESCRIBING INFORMATION. Novo Nordisk Accessed October 22, 2025. https://www.novo-pi.com/ozempic.pdf