Proper medication dosing is essential for maximizing treatment effectiveness while minimizing risks and side effects. According to a study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association, precision dosing significantly improves treatment outcomes and patient adherence, reinforcing the importance of following prescribed regimens.
Among the various osteoporosis treatments available, Prolia (denosumab) is a widely prescribed option for postmenopausal women at high risk of fracture. When administered correctly, Prolia helps increase bone mass and reduce fracture risk by inhibiting osteoclast activity, slowing bone resorption.
In this article, we will explore the Prolia dosing regimen, including its recommended schedule, benefits, potential risks, and best practices for administration, ensuring safe and effective osteoporosis treatment.
Key Takeaways on Prolia Injection Treatment
- The standard dosing recommendation for Prolia is a 60 mg subcutaneous injection every six months.
- To maximize effectiveness, Prolia should be administered in the upper arm, upper thigh, or abdomen after it has reached room temperature.
- Patients with severe renal impairment should have their calcium and mineral levels closely monitored, as they are at increased risk for complications.
- Healthcare providers should educate patients on the significance of adhering to the Prolia dosing schedule to maintain bone density and reduce fracture risk.
About: Medica Depot is your trusted all-in-one supplier, offering a range of high-quality medical injectables and supplies. Our sales representatives can advise you on how to buy Prolia online today! Whether for health professionals, plastic surgeons, dermatologists, licensed estheticians, or other specialists, we can offer genuine, brand-name products you may need. With Medica Depot, we prioritize serving you better to improve the patient’s quality of life.
Recommended Prolia Dosing Schedule
Prolia for osteoporosis is an FDA-approved treatment specifically designed for postmenopausal women and men at high risk of fractures. While Prolia has a proven safety and efficacy profile, proper administration and adherence to the prescribed dosing schedule are crucial for maximizing its effectiveness.
When comparing Prolia vs. Evenity or other osteoporosis treatments, Prolia stands out for its convenient dosing schedule. It requires only one injection every six months duration, making it a low-maintenance option for long-term bone health.
The recommended Prolia dosing regimen consists of a 60 mg subcutaneous injection administered in the upper arm, upper thigh, or abdomen.
Strict adherence to this twice-yearly dosing duration schedule is essential to prevent bone loss, reduce fracture risk, and maintain optimal bone density. Consistent administration ensures Prolia delivers sustained therapeutic benefits, helping patients receiving the treatment effectively manage or treat osteoporosis.
Timing Considerations for Best Results
Healthcare professionals and patients need to understand the importance of the recommended timing for Prolia injections. Missed doses or abrupt discontinuation of Prolia without an expert’s recommendation or prescription may result in a rapid decline in bone density and risk of fractures.
Administration and Handling of Prolia Injections
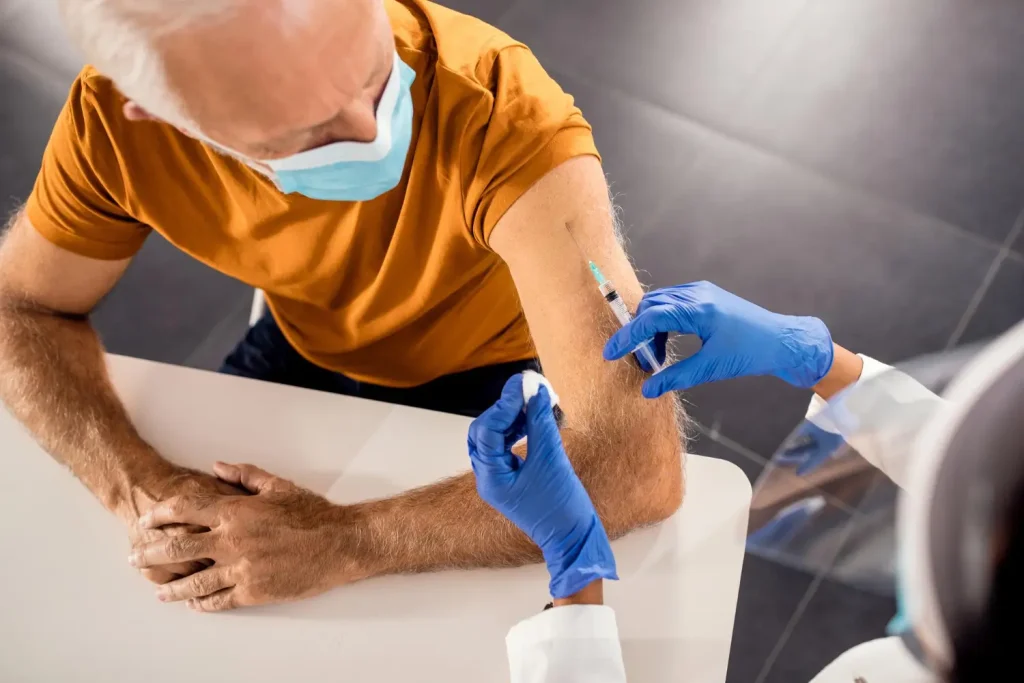
Prolia is a clear, colorless to pale yellow solution that may contain trace amounts of translucent to white proteinaceous particles. Before administration, providers must remove Prolia from the refrigerator and allow it to reach room temperature (up to 25°C/77°F) by standing it in its original container for approximately 15 to 30 minutes.
The Prolia single-dose prefilled syringe has a green safety guard that should be manually activated immediately after administering the injection. Furthermore, Amgen’s Prolia has other administration and handling requirements.
- Proper Injection Sites and Techniques: To administer Prolia, practitioners and patients can select an appropriate injection site from the upper arm, upper thigh, or abdomen. Carefully insert the needle and deliver the entire solution subcutaneously, ensuring that the injection is not administered into a muscle or blood vessel. These practitioners can utilize their preferred injection technique for ease of administration.
- Storage Requirements and Stability Concerns: Store Prolia in its original carton in a refrigerator at temperatures between 2°C and 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Ensure that Prolia is not frozen and protected from direct light and heat. Avoid vigorous shaking to maintain the medication’s stability and effectiveness.
Safety Precautions for Healthcare Providers
Patients must seek licensed healthcare providers with comprehensive knowledge about Prolia treatments and are appropriately trained to administer this osteoporosis treatment. The safety precautions of this prescription injection require consistent monitoring to prevent further complications and conduct prompt action.
- Severe Hypocalcemia (low calcium levels) and Mineral Metabolism Changes
- Drug Products with the Same Active Ingredient
- Hypersensitivity
- Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
- Serious Infections
- Suppression of Bone Turnover
Healthcare providers must ensure patients receive adequate calcium and vitamin D supplementation when taking Prolia. Moreover, they should equip patients with adequate information and education about the potential symptoms that may require immediate medical attention.
Adjustments and Managing Missed Doses

For patients with renal impairment, no dosage adjustment is necessary. However, patients receiving Prolia and with severe renal impairment (CrCl < 30 mL/min) are at an increased risk for hypocalcemia. It is highly recommended that these patients’ calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium levels are clinically monitored to ensure their safety. Practitioners should also evaluate the risks and benefits before initiating Prolia osteoporosis therapy.
Patients who miss a scheduled dose of Prolia should promptly contact their healthcare provider for guidance. They must get the missed dose immediately without doubling it at the next scheduled administration.
Additionally, discontinuing Prolia without transitioning to an alternative antiresorptive therapy can cause a swift decline in bone mineral density, increasing the risk of rebound-associated fractures. Consistently taking this treatment can maintain the effects of Prolia on bone improvements. Moreover, it is imperative to closely monitor patients and consider alternative treatments to mitigate these adverse effects.
Conclusion
The Prolia dosing regimen consists of a 60 mg subcutaneous injection every six months, a schedule that is crucial for effectively managing osteoporosis and reducing fracture risk in postmenopausal women and high-risk men. Consistent administration ensures optimal bone protection and enhances the medication’s overall effectiveness.
Maintaining open communication between healthcare providers and patients plays a key role in treatment success. Reinforcing the importance of adherence, addressing concerns about side effects, and offering dosing reminders can help patients stay committed to their treatment plan. With the right support, Prolia can provide long-term benefits for bone health and fracture prevention.
FAQs
1. What is the recommended dosing schedule for Prolia?
The recommended dosing for Prolia is a 60 mg subcutaneous injection administered once every six months. This schedule is essential for maintaining bone density and reducing fracture risk.
2. How do practitioners administer Prolia?
They inject Prolia into the upper arm, upper thigh, or abdomen. Before injection, it should reach room temperature for about 15 to 30 minutes. Practitioners should also ensure that they inject the entire Prolia solution subcutaneously and not into a muscle or blood vessel.
3. What should patients do if they miss a dose of Prolia?
If patients miss a scheduled dose of Prolia, you should contact your healthcare provider for advice. Generally, it’s best to get the missed dose as soon as possible, but avoid doubling up on the next scheduled dose.
References
- Maxfield, K., & Zineh, I. (2021). Precision Dosing. JAMA Network, 325(15), 1505. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.1004
- HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION Prolia ® (denosumab). (n.d.). Retrieved February 20, 2025, from https://www.pi.amgen.com/-/media/Project/Amgen/Repository/pi-amgen-com/Prolia/prolia_pi.pdf