According to a study by Deshpande et al. (2016), over half of individuals with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis (OA) are under 65, highlighting that around 14 million people in this age group are affected. Many of these cases are advanced, underscoring the need for effective treatment options.
Knee osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that can lead to chronic pain, swelling, and limited mobility, significantly impacting quality of life. In the search for innovative relief, treatments like Cingal and Durolane have emerged as promising options. Both of these single-injection therapies utilize the benefits of sodium hyaluronate to provide pain relief and improved function for knee OA sufferers.
This article will provide a detailed comparison of Cingal vs Durolane, examining their active ingredients, effectiveness, administration protocols, and potential side effects to help you understand how each may address knee OA.
Key Takeaways
- Numerous regulatory agencies worldwide have approved different viscosupplements to help knee OA patients manage pain, inflammation, and restricted mobility.
- Cingal’s effectiveness stems from its two well-known active ingredients for treating knee OA: hyaluronic acid and corticosteroid.
- Durolane highlights that its injection features non-animal stabilized hyaluronic acid.
- Despite having similar treatment protocols and administration, Cingal and Durolane require different dosages. Cingal needs 4 mL per knee joint, while Durolane requires 3 mL for one knee.
About: Medica Depot is your trusted all-in-one supplier, offering a range of high-quality medical injectables and supplies. Buy Cingal at Medica Depot today! Whether for health professionals, plastic surgeons, dermatologists, licensed estheticians, or other specialists, we can offer genuine, brand-name products you may need. With Medica Depot, we prioritize serving you better to improve the patient’s quality of life.
Understanding Cingal and Durolane
Viscosupplementation is an increasingly popular, effective solution for managing the chronic symptoms of osteoarthritis (OA), including pain, inflammation, and restricted mobility. Globally, many viscosupplement brands are approved to help knee OA patients.
Cingal, developed by Anika Therapeutics, offers a dual-action approach. Its formulation combines hyaluronic acid with a corticosteroid, providing both long-lasting joint lubrication and immediate symptom relief. This single-injection treatment aims to restore the viscoelasticity of the joint’s synovial fluid, allowing for both short-term and sustained pain relief.
Durolane also follows a single-injection regimen and is designed to improve pain and joint function in knee OA patients. Unlike Cingal, Durolane relies solely on high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid, which provides joint lubrication and cushioning without additional components. However, this treatment may take a bit longer to deliver initial relief than Cingal.
Active Ingredients
Despite harnessing the potency of hyaluronic acid, Cingal and Durolane’s formulations differ. These unique formulations affect the longevity and effectiveness of both these viscosupplements. Understanding these active ingredients can help individuals make more informed treatment decisions.
Cingal combines two active ingredients specifically suited for OA symptom management: hyaluronic acid and a corticosteroid. The proprietary, cross-linked hyaluronic acid offers long-lasting relief by improving joint lubrication, while the corticosteroid component provides immediate anti-inflammatory benefits, helping to reduce pain and swelling soon after treatment.
On the other hand, Durolane focuses solely on non-animal stabilized hyaluronic acid. This formulation is specially stabilized to resist degradation within the joint, extending its effectiveness for longer-lasting pain relief and enhanced joint lubrication. While Durolane doesn’t contain a corticosteroid, its durability makes it a strong choice for patients seeking sustained relief from OA symptoms.
Administration Protocols
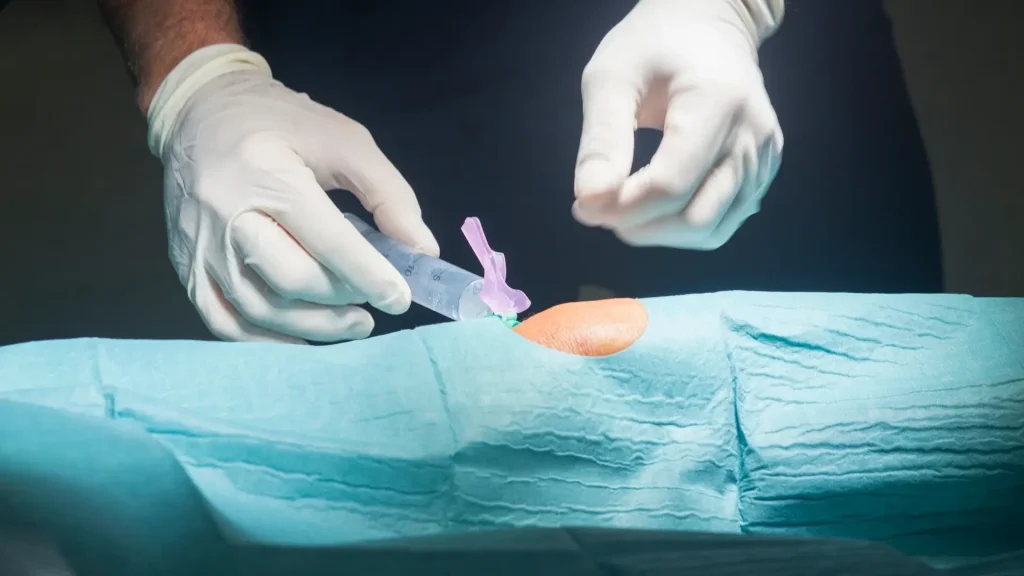
For safety and effectiveness, Cingal and Durolane injections should only be administered by qualified healthcare professionals. Seeking treatment from a trusted medical provider helps ensure patients receive the full benefit and long-lasting relief from knee osteoarthritis (OA) symptoms.
Both Cingal and Durolane are designed to work with just a single injection directly into the affected knee joint. This intra-articular injection requires sterile conditions and careful technique; for example, any excess joint fluid is typically drained before the injection to allow for better absorption of the viscosupplement.
While they share a similar administration process, Cingal and Durolane differ in dosage. Cingal’s recommended dose is 4 mL per knee, while Durolane requires 3 mL. These slight differences in volume relate to their unique formulations, each designed to provide optimal cushioning and lubrication in the knee joint.
Effectiveness in Treating Osteoarthritis
Cingal’s clinical study showed that Cingal provides faster knee pain relief than HA alone, significantly reducing pain at weeks 1 and 3. Patients experienced long-lasting relief and statistically significant pain reduction through week 26 compared to saline. Cingal consistently outperformed saline in pain, stiffness, physical function, and global assessment measurements.
Systematic clinical evidence by Leighton et al. (2018) demonstrated through clinical studies that a single injection of NASHA offers enduring relief for knee osteoarthritis (OA) symptoms. Additionally, Durolane exhibits excellent biocompatibility, leading to minimal adverse events with this intra-articular therapy.
Potential Side Effects
In addition to their benefits and efficacy, healthcare professionals must explain the potential risks associated with these treatments. Understanding the side effects that may occur after these single-injection treatments is crucial when comparing Cingal vs Durolane or Cingal vs Monovisc.
The common Durolane and Cingal side effects often range between mild and moderate and can subside independently once the body adapts to the medicine in a few days to a week. However, if these persist, patients must consult their healthcare providers for proper management.
- Typical Cingal Side Effects: Injection site pain, joint pain, rash, redness or swelling
- Typical Durolane Side Effects: Transient pain, swelling, and stiffness localized to the joint.
Improper administration, wrong dosage and protocol, or continuing treatment despite the contraindications may cause patients to experience rare and severe reactions. These include allergic reactions, infections, or severe joint pain, necessitating immediate medical attention for prompt action.
Patient Experiences
Unfortunately, limited patient experience online underscores Cingal’s effectiveness in delivering symptomatic relief to knee osteoarthritis (OA) patients. Nonetheless, a medical professional has shared a positive experience that showcases the efficacy of Cingal’s injection regimen in their five patients.

Meanwhile, Durolane has more testimonials from treated patients who have shared their impressive relief journey with the single-injection treatment. A patient, Mario Huet, received Durolane, which slowed the progression of their condition and allowed them to return to their active lifestyle.

Conclusion
Cingal and Durolane offer effective treatment options for individuals battling knee osteoarthritis. Cingal combines hyaluronic acid with a corticosteroid, providing rapid relief along with sustained pain and inflammation reduction. In contrast, Durolane relies on non-animal stabilized hyaluronic acid, focusing on joint lubrication and lasting comfort.
Choosing between Cingal and Durolane depends on the patient’s specific needs and treatment goals. By understanding the differences in formulation, dosage, and how each injection works, patients can make a more informed decision to better manage their osteoarthritis symptoms and improve their quality of life.
FAQs
1. What are Cingal and Durolane used for?
Cingal and Durolane treat knee osteoarthritis (OA) by relieving pain and improving joint mobility through viscosupplementation.
2. How do Cingal and Durolane differ in their formulations?
Cingal contains hyaluronic acid and a corticosteroid for immediate and long-lasting relief, while Durolane utilizes non-animal stabilized hyaluronic acid for its lubricating effects.
3. What are the administration protocols for Cingal and Durolane?
Cingal and Durolane require a single intra-articular injection into the affected knee joint, with 4 mL of Cingal and 3 mL of Durolane needed per knee.
References
- Deshpande, B. R., Katz, J. N., Solomon, D. H., Yelin, E. H., Hunter, D. J., Messier, S. P., Suter, L. G., & Losina, E. (2016). Number of Persons With Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis in the US: Impact of Race and Ethnicity, Age, Sex, and Obesity. Arthritis care & research, 68(12), 1743–1750. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.22897
- Leighton, R., Fitzpatrick, J., Smith, H., Crandall, D., Flannery, C. R., & Conrozier, T. (2018). Systematic clinical evidence review of NASHA (Durolane hyaluronic acid) for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Open access rheumatology: research and reviews, 10, 43–54. https://doi.org/10.2147/OARRR.S162127